Page 70 - E-Bussiness and E-Commerce Management Strategy, Implementation, and Practice
P. 70
M01_CHAF9601_04_SE_C01.QXD:D01_CHAF7409_04_SE_C01.QXD 16/4/09 11:02 Page 37
Chapter 1 Introduction to e-business and e-commerce 37
Stage 6. Stage 6. Supply
Site optimization chain optimization
Stage 5. Stage 5.
Relationship building Integrate databases
Stage 4. Stage 4.
Online ordering Online ordering
Stage 3. Stage 3.
Interactive site Online catalogues
Stage 2. Stage 2.
Brochureware site Stock availability
Stage 1. Stage 1.
E-mail marketing Review suppliers
Sell-side e-commerce Buy-side e-commerce
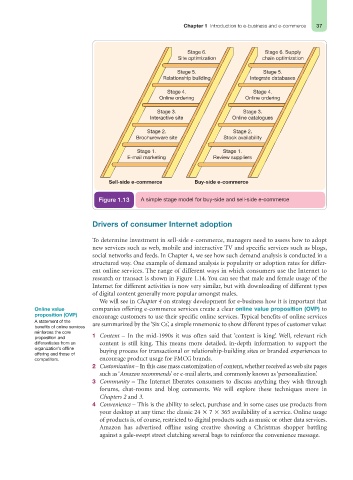
Figure 1.13 A simple stage model for buy-side and sell-side e-commerce
Drivers of consumer Internet adoption
To determine investment in sell-side e-commerce, managers need to assess how to adopt
new services such as web, mobile and interactive TV and specific services such as blogs,
social networks and feeds. In Chapter 4, we see how such demand analysis is conducted in a
structured way. One example of demand analysis is popularity or adoption rates for differ-
ent online services. The range of different ways in which consumers use the Internet to
research or transact is shown in Figure 1.14. You can see that male and female usage of the
Internet for different activities is now very similar, but with downloading of different types
of digital content generally more popular amongst males.
We will see in Chapter 4 on strategy development for e-business how it is important that
Online value companies offering e-commerce services create a clear online value proposition (OVP) to
proposition (OVP) encourage customers to use their specific online services. Typical benefits of online services
A statement of the
benefits of online services are summarized by the ‘Six Cs’, a simple mnemonic to show different types of customer value:
reinforces the core
proposition and 1 Content – In the mid-1990s it was often said that ‘content is king’. Well, relevant rich
differentiates from an content is still king. This means more detailed, in-depth information to support the
organization’s offline buying process for transactional or relationship-building sites or branded experiences to
offering and those of
competitors. encourage product usage for FMCG brands.
2 Customization – In this case mass customization of content, whether received as web site pages
such as ‘Amazon recommends’ or e-mail alerts, and commonly known as ‘personalization’.
3 Community – The Internet liberates consumers to discuss anything they wish through
forums, chat-rooms and blog comments. We will explore these techniques more in
Chapters 2 and 3.
4 Convenience – This is the ability to select, purchase and in some cases use products from
your desktop at any time: the classic 24 × 7 × 365 availability of a service. Online usage
of products is, of course, restricted to digital products such as music or other data services.
Amazon has advertised offline using creative showing a Christmas shopper battling
against a gale-swept street clutching several bags to reinforce the convenience message.