Page 174 - Earth's Climate Past and Future
P. 174
150 PART III • Orbital-Scale Climate Change
Precessional magnetic evidence from volcanic rocks indicate that
Eccentricity insolation the Newark Basin was located in the tropics 200 Myr
0.00 0.03 0.06 Low High ago, about 10° of latitude north of the equator (see
20,000 Figure 8-14). Because of its tropical location, the Newark
years Basin was dominated by precessional insolation changes,
similar to those in modern North Africa and southern
Asia. Because the basin was far from the ocean, its climate
100,000 100,000 was relatively arid, but enough moisture arrived to create
Time years years a lake that varied greatly in size over time.
Evidence preserved in a thick (> 7000 m) sequence of
lake sediments shows that the size of this lake fluctuated
at a tempo near 20,000 years. Several layers of molten
magma that intruded into the lakebed sequence and
quickly cooled have been dated by radiometric methods.
400,000 400,000
years years These dates show that the lakebed sequence was
deposited over an interval of at least 20 Myr centered
near 200 Myr ago.
This estimate is confirmed by the presence of
fine laminations (varves) in parts of the sequence. The
varves are tiny (0.2–0.3 mm) couplets of alternating light
Threshold
value
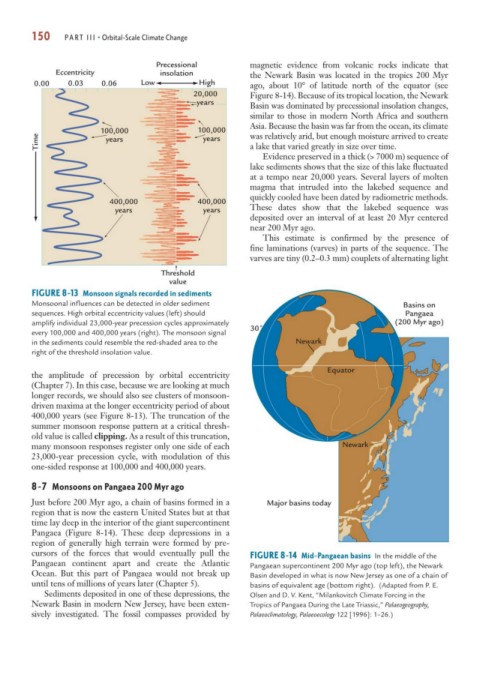
FIGURE 8-13 Monsoon signals recorded in sediments
Monsoonal influences can be detected in older sediment Basins on
sequences. High orbital eccentricity values (left) should Pangaea
amplify individual 23,000-year precession cycles approximately (200 Myr ago)
30˚
every 100,000 and 400,000 years (right). The monsoon signal
in the sediments could resemble the red-shaded area to the Newark
right of the threshold insolation value.
Equator
the amplitude of precession by orbital eccentricity
(Chapter 7). In this case, because we are looking at much
longer records, we should also see clusters of monsoon-
driven maxima at the longer eccentricity period of about
400,000 years (see Figure 8-13). The truncation of the
summer monsoon response pattern at a critical thresh-
old value is called clipping. As a result of this truncation,
many monsoon responses register only one side of each Newark
23,000-year precession cycle, with modulation of this
one-sided response at 100,000 and 400,000 years.
8-7 Monsoons on Pangaea 200 Myr ago
Just before 200 Myr ago, a chain of basins formed in a Major basins today
region that is now the eastern United States but at that
time lay deep in the interior of the giant supercontinent
Pangaea (Figure 8-14). These deep depressions in a
region of generally high terrain were formed by pre-
cursors of the forces that would eventually pull the FIGURE 8-14 Mid-Pangaean basins In the middle of the
Pangaean continent apart and create the Atlantic Pangaean supercontinent 200 Myr ago (top left), the Newark
Ocean. But this part of Pangaea would not break up Basin developed in what is now New Jersey as one of a chain of
until tens of millions of years later (Chapter 5). basins of equivalent age (bottom right). (Adapted from P. E.
Sediments deposited in one of these depressions, the Olsen and D. V. Kent, “Milankovitch Climate Forcing in the
Newark Basin in modern New Jersey, have been exten- Tropics of Pangaea During the Late Triassic,” Palaeogeography,
sively investigated. The fossil compasses provided by Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 122 [1996]: 1–26.)