Page 128 - Educational Technology A Primer for the 21st Century
P. 128
118 7 Social Learning Perspective of Educational Technology
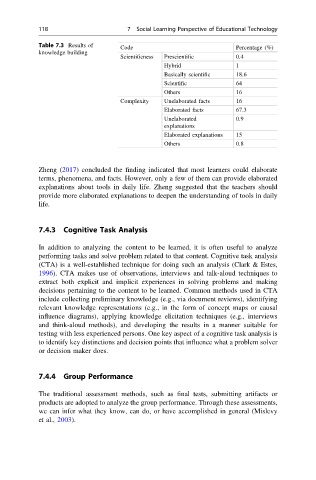
Table 7.3 Results of
Code Percentage (%)
knowledge building
Scientificness Prescientific 0.4
Hybrid 1
Basically scientific 18.6
Scientific 64
Others 16
Complexity Unelaborated facts 16
Elaborated facts 67.3
Unelaborated 0.9
explanations
Elaborated explanations 15
Others 0.8
Zheng (2017) concluded the finding indicated that most learners could elaborate
terms, phenomena, and facts. However, only a few of them can provide elaborated
explanations about tools in daily life. Zheng suggested that the teachers should
provide more elaborated explanations to deepen the understanding of tools in daily
life.
7.4.3 Cognitive Task Analysis
In addition to analyzing the content to be learned, it is often useful to analyze
performing tasks and solve problem related to that content. Cognitive task analysis
(CTA) is a well-established technique for doing such an analysis (Clark & Estes,
1996). CTA makes use of observations, interviews and talk-aloud techniques to
extract both explicit and implicit experiences in solving problems and making
decisions pertaining to the content to be learned. Common methods used in CTA
include collecting preliminary knowledge (e.g., via document reviews), identifying
relevant knowledge representations (e.g., in the form of concept maps or causal
influence diagrams), applying knowledge elicitation techniques (e.g., interviews
and think-aloud methods), and developing the results in a manner suitable for
testing with less experienced persons. One key aspect of a cognitive task analysis is
to identify key distinctions and decision points that influence what a problem solver
or decision maker does.
7.4.4 Group Performance
The traditional assessment methods, such as final tests, submitting artifacts or
products are adopted to analyze the group performance. Through these assessments,
we can infer what they know, can do, or have accomplished in general (Mislevy
et al., 2003).