Page 79 - Educational Technology A Primer for the 21st Century
P. 79
68 4 Systems Perspective of Educational Technology
that provides oxygen, water, and nourishment (inputs necessary for life), and there
are outputs from the human body to the environment as well.
4.2 Education Systems
Roger Kaufman (1972) was one of the first to apply a systems approach to edu-
cation. An education system is a man-made system and can be considered as a
subsystem of the society in which it exists. One might think of an education system
as taking inputs from the society (e.g., students) and providing outputs to society
(e.g., graduates). Moreover, an education system could be conceptualized as a
collection of subsystems, such as a school system, a curricular system, a grading
system, and so on.
Elements of an Education System
According to the characteristics of the system, the education system can be cate-
gorized to different levels: (1) macro-level: state, social education system;
(2) meso-level: community and school education system; (3) micro-level: teaching
process, learning process, media development, and other education system. The
school system may be treated as a subsystem of the education system or a system
complete in itself (Mangal & Mangal, 2009). In this chapter, we mainly focus on
the school education system at the meso-level, and the structure of the education
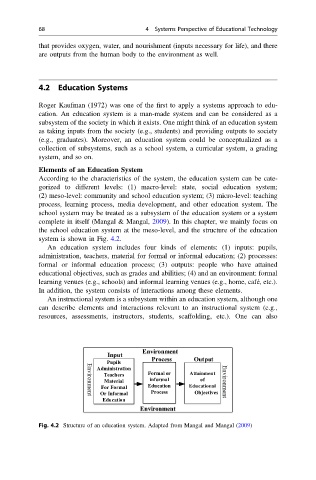
system is shown in Fig. 4.2.
An education system includes four kinds of elements: (1) inputs: pupils,
administration, teachers, material for formal or informal education; (2) processes:
formal or informal education process; (3) outputs: people who have attained
educational objectives, such as grades and abilities; (4) and an environment: formal
learning venues (e.g., schools) and informal learning venues (e.g., home, café, etc.).
In addition, the system consists of interactions among these elements.
An instructional system is a subsystem within an education system, although one
can describe elements and interactions relevant to an instructional system (e.g.,
resources, assessments, instructors, students, scaffolding, etc.). One can also
Input Environment
Pupils Process Output
Administration
Teachers Formal or Attainment
Material informal of Environment
For Formal Education Educational
Or Informal Process Objectives
Environment
Education
Environment
Fig. 4.2 Structure of an education system. Adapted from Mangal and Mangal (2009)