Page 30 - Electric Machinery Fundamentals
P. 30
6 ELECTRIC MACHINERY FUNDAMENTALS
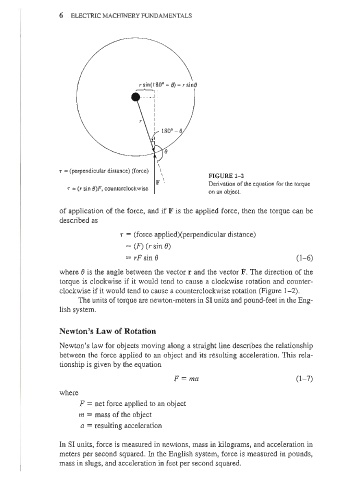
r sin(l 80° - (J) = rsinO
,..-'----"
_J ,
,
,
,
,
r ,
,
,
,
T = (perpendicular distance) (force) ,
FIGURE 1- 2
F '. Derivation of the equation for the torque
T = (r sin (J)F, counterclockwise
on an object.
of application of the force, and if F is the applied force, then the torque can be
described as
T = (force applied)(perpendicular distance)
= (F) (r sin 0)
= rF sin 0 (1- 6)
where 0 is the angle between the vector r and the vector F. The direction of the
torque is clockwise if it would tend to cause a clockwise rotation and counter-
clockwise if it would tend to cause a counterclockwise rotation (Figure 1-2).
The units of torque are newton-meters in SI units and pound-feet in the Eng-
lish system.
Newton's Law of Rotation
Newton's law for objects moving along a straight line describes the relationship
between the force applied to an object and its resulting acceleration. This rela-
tionship is given by the equation
F =ma (1-7)
where
F = net force applied to an object
In = mass of the object
a = resulting acceleration
In SI units, force is measured in newtons, mass in kilograms, and acceleration in
meters per second squared. In the English system, force is measured in pounds,
mass in slugs, and acceleration in feet per second squared.