Page 135 - Electrical Engineering Dictionary
P. 135
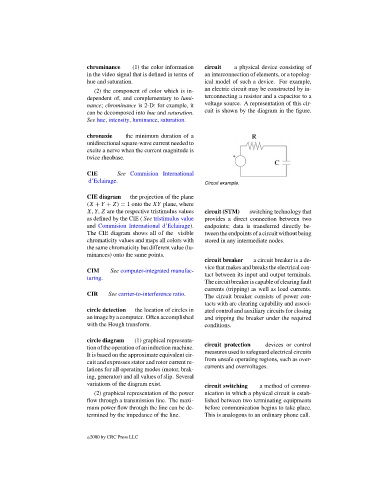
chrominance (1) the color information circuit a physical device consisting of
in the video signal that is defined in terms of an interconnection of elements, or a topolog-
hue and saturation. ical model of such a device. For example,
(2) the component of color which is in- an electric circuit may be constructed by in-
dependent of, and complementary to lumi- terconnecting a resistor and a capacitor to a
nance; chrominance is 2-D: for example, it voltage source. A representation of this cir-
can be decomposed into hue and saturation. cuit is shown by the diagram in the figure.
See hue, intensity, luminance, saturation.
chronaxie the minimum duration of a
unidirectional square-wave current needed to
excite a nerve when the current magnitude is
twice rheobase.
CIE See Commision International
d’Eclairage.
Circuit example.
CIE diagram the projection of the plane
(X + Y + Z) = 1 onto the XY plane, where
X, Y, Z are the respective tristimulus values circuit (STM) switching technology that
as defined by the CIE ( See tristimulus value provides a direct connection between two
and Commision International d’Eclairage). endpoints; data is transferred directly be-
The CIE diagram shows all of the visible tween the endpoints of a circuit without being
chromaticity values and maps all colors with stored in any intermediate nodes.
the same chromaticity but different value (lu-
minances) onto the same points.
circuit breaker a circuit breaker is a de-
vice that makes and breaks the electrical con-
CIM See computer-integrated manufac-
tact between its input and output terminals.
turing.
Thecircuitbreakeriscapableofclearingfault
currents (tripping) as well as load currents.
CIR See carrier-to-interference ratio.
The circuit breaker consists of power con-
tacts with arc clearing capability and associ-
circle detection the location of circles in ated control and auxiliary circuits for closing
an image by a computer. Often accomplished and tripping the breaker under the required
with the Hough transform. conditions.
circle diagram (1) graphical representa-
circuit protection devices or control
tion of the operation of an induction machine.
measures used to safeguard electrical circuits
It is based on the approximate equivalent cir-
from unsafe operating regions, such as over-
cuit and expresses stator and rotor current re-
currents and overvoltages.
lations for all operating modes (motor, brak-
ing, generator) and all values of slip. Several
variations of the diagram exist.
circuit switching a method of commu-
(2) graphical representation of the power nication in which a physical circuit is estab-
flow through a transmission line. The maxi- lished between two terminating equipments
mum power flow through the line can be de- before communication begins to take place.
termined by the impedance of the line. This is analogous to an ordinary phone call.
c
2000 by CRC Press LLC