Page 204 - Electromechanical Devices and Components Illustrated Sourcebook
P. 204
166 Electromechanical Devices & Components Illustrated Sourcebook
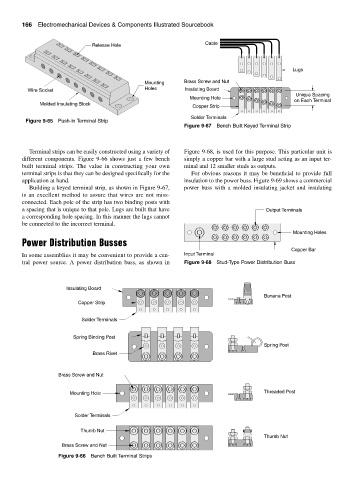
Cable
Release Hole
Lugs
Mounting Brass Screw and Nut
Holes Insulating Board
Wire Socket
Unique Spacing
Mounting Hole
on Each Terminal
Molded Insulating Block
Copper Strip
Solder Terminals
Figure 9-65 Push-in Terminal Strip
Figure 9-67 Bench Built Keyed Terminal Strip
Terminal strips can be easily constructed using a variety of Figure 9-68, is used for this purpose. This particular unit is
different components. Figure 9-66 shows just a few bench simply a copper bar with a large stud acting as an input ter-
built terminal strips. The value in constructing your own minal and 12 smaller studs as outputs.
terminal strips is that they can be designed specifically for the For obvious reasons it may be beneficial to provide full
application at hand. insulation to the power buss. Figure 9-69 shows a commercial
Building a keyed terminal strip, as shown in Figure 9-67, power buss with a molded insulating jacket and insulating
is an excellent method to assure that wires are not miss-
connected. Each pole of the strip has two binding posts with
a spacing that is unique to that pole. Lugs are built that have Output Terminals
a corresponding hole spacing. In this manner the lugs cannot
be connected to the incorrect terminal.
Mounting Holes
Power Distribution Busses
Copper Bar
In some assemblies it may be convenient to provide a cen- Input Terminal
tral power source. A power distribution buss, as shown in Figure 9-68 Stud-Type Power Distribution Buss
Insulating Board
Banana Post
Copper Strip
Solder Terminals
Spring Binding Post
Spring Post
Brass Rivet
Brass Screw and Nut
Mounting Hole Threaded Post
Solder Terminals
Thumb Nut
Thumb Nut
Brass Screw and Nut
Figure 9-66 Bench Built Terminal Strips