Page 92 - Electronic Commerce
P. 92
Technology Infrastructure: The Internet and the World Wide Web
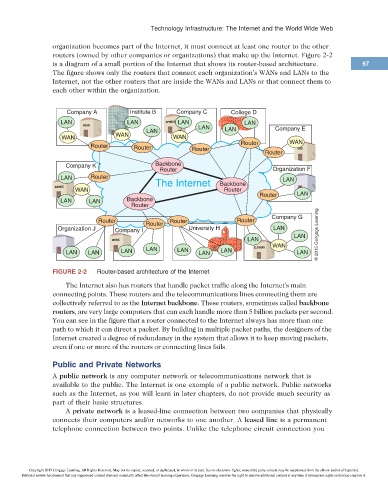
organization becomes part of the Internet, it must connect at least one router to the other
routers (owned by other companies or organizations) that make up the Internet. Figure 2-2
is a diagram of a small portion of the Internet that shows its router-based architecture. 67
The figure shows only the routers that connect each organization’s WANs and LANs to the
Internet, not the other routers that are inside the WANs and LANs or that connect them to
each other within the organization.
Company A Institute B Company C College D
LAN LAN LAN LAN
LAN LAN Company E
LAN
WAN
WAN WAN
Router WAN
Router Router Router
Router
Company K Backbone
Router Organization F
LAN Router LAN
The Internet Backbone
WAN Router
Router LAN
LAN LAN Backbone
Router
Company G Learning
Router Router Router
Router
Organization J Company I University H LAN
LAN Cengage
LAN
WAN
LAN LAN LAN LAN LAN LAN LAN LAN 2015
©
FIGURE 2-2 Router-based architecture of the Internet
The Internet also has routers that handle packet traffic along the Internet’smain
connecting points. These routers and the telecommunications lines connecting them are
collectively referred to as the Internet backbone. These routers, sometimes called backbone
routers, are very large computers that can each handle more than 5 billion packets per second.
You can see in the figure that a router connected to the Internet always has more than one
path to which it can direct a packet. By building in multiple packet paths, the designers of the
Internet created a degree of redundancy in the system that allows it to keep moving packets,
even if one or more of the routers or connecting lines fails.
Public and Private Networks
A public network is any computer network or telecommunications network that is
available to the public. The Internet is one example of a public network. Public networks
such as the Internet, as you will learn in later chapters, do not provide much security as
part of their basic structures.
A private network is a leased-line connection between two companies that physically
connects their computers and/or networks to one another. A leased line is a permanent
telephone connection between two points. Unlike the telephone circuit connection you
Copyright 2015 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.