Page 188 -
P. 188
Homework Problem
Pb. 6.55 Plot the magnitude and the phase of theTransfer Function given in
Eq. (6.87) as a function of ω, for LC = 1, RC = 3.
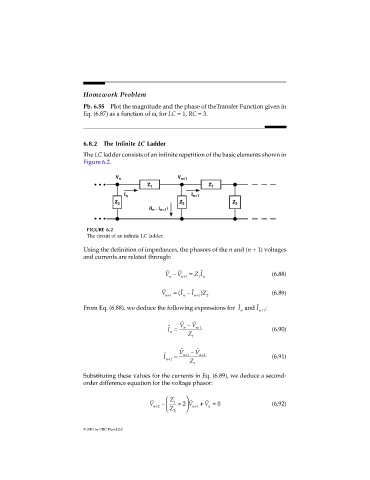
6.8.2 The Infinite LC Ladder
The LC ladder consists of an infinite repetition of the basic elements shown in
Figure 6.2.
V n V n+1
Z 1 Z 1
I n I n+1
Z 2 Z 2 Z 2
(I n – I n+1 )
FIGURE 6.2
The circuit of an infinite LC ladder.
Using the definition of impedances, the phasors of the n and (n + 1) voltages
and currents are related through:
˜
V − V = Z I ˜ (6.88)
˜
n n+1 1 n
˜
˜
V = (I − I ˜ )Z (6.89)
n+1 n n+1 2
˜
From Eq. (6.88), we deduce the following expressions for I and ˜ I :
n n+1
V − V
˜
˜
I = n n+1 (6.90)
˜
n
Z
1
˜
V − V ˜
˜ I = n+1 n+2 (6.91)
n+1
Z
1
Substituting these values for the currents in Eq. (6.89), we deduce a second-
order difference equation for the voltage phasor:
Z
˜
˜
V − 1 + 2 V ˜ + V = 0 (6.92)
n+2 n+1 n
Z 2
© 2001 by CRC Press LLC