Page 74 -
P. 74
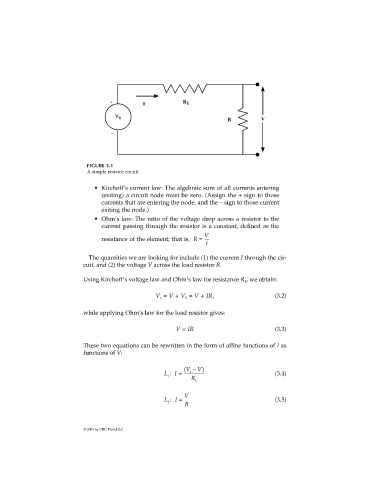
+ R
I 1
V s R V
_
FIGURE 3.1
A simple resistor circuit.
• Kirchoff’s current law: The algebraic sum of all currents entering
(exiting) a circuit node must be zero. (Assign the + sign to those
currents that are entering the node, and the – sign to those current
exiting the node.)
• Ohm’s law: The ratio of the voltage drop across a resistor to the
current passing through the resistor is a constant, defined as the
resistance of the element; that is, R = V
I
The quantities we are looking for include (1) the current I through the cir-
cuit, and (2) the voltage V across the load resistor R.
Using Kirchoff’s voltage law and Ohm’s law for resistance R , we obtain:
1
V = V + V = V + IR 1 (3.2)
1
s
while applying Ohm’s law for the load resistor gives:
V = IR (3.3)
These two equations can be rewritten in the form of affine functions of I as
functions of V:
s
L : I = ( V − V) (3.4)
1
R
1
L : I = V (3.5)
2
R
© 2001 by CRC Press LLC