Page 133 - Bruno Linder Elementary Physical Chemistry
P. 133
August 18, 2010 11:37 9in x 6in b985-ch11 Elementary Physical Chemistry
118 Elementary Physical Chemistry
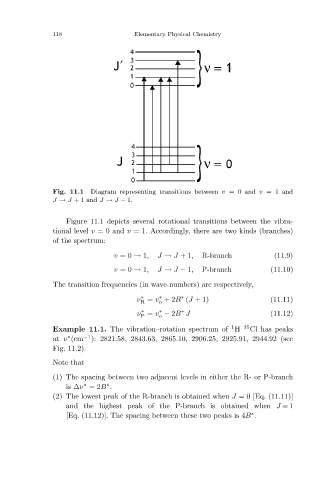
Diagram representing transitions between v =0 and v =1 and
Fig. 11.1
J → J +1 and J → J − 1.
Figure 11.1 depicts several rotational transitions between the vibra-
tional level v =0 and v = 1. Accordingly, there are two kinds (branches)
of the spectrum:
v =0 → 1, J → J +1, R-branch (11.9)
v =0 → 1, J → J − 1, P-branch (11.10)
The transition frequencies (in wave-numbers) are respectively,
∗
ν = v +2B (J + 1) (11.11)
∗
∗
o
R
ν = v − 2B J (11.12)
∗
∗
∗
o
P
1
Example 11.1. The vibration–rotation spectrum of H 35 Cl has peaks
at ν (cm −1 ): 2821.58, 2843.63, 2865.10, 2906.25, 2925.91, 2944.92 (see
∗
Fig. 11.2).
Note that
(1) The spacing between two adjacent levels in either the R- or P-branch
is ∆ν =2B .
∗
∗
(2) The lowest peak of the R-branch is obtained when J = 0 [Eq. (11.11)]
and the highest peak of the P-branch is obtained when J =1
∗
[Eq. (11.12)]. The spacing between these two peaks is 4B .