Page 20 - Bruno Linder Elementary Physical Chemistry
P. 20
August 18, 2010 11:35 9in x 6in b985-ch01 Elementary Physical Chemistry
State of Matter. Properties of Gases 5
the sum of the partial pressures. That is,
P =Σ iP i. =Σ in i RT/V = RT Σ in i/V = nRT/V (1.10a)
where n =Σ i n i is the total number of moles. Accordingly,
P i /P = n i/n = x i or P i = x i P (1.10b)
[This relation is strictly valid for ideal gases.]
1.7. The Kinetic Theory of Gases
The theory is based on the following assumptions:
1. There are N molecules, each of weight m.
2. Molecules are in constant motion. They collide with each other and with
the walls of the container.
3. In ideal gases, molecules do not interact with each other.
4. The volume of molecules is negligible compared to the volume of
container.
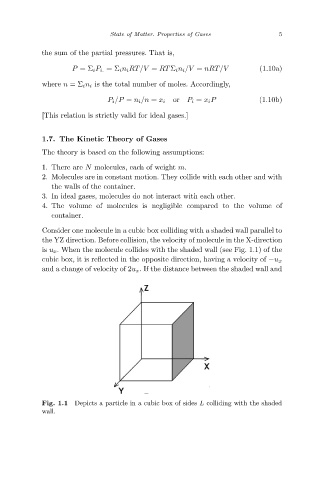
Consider one molecule in a cubic box colliding with a shaded wall parallel to
the YZ direction. Before collision, the velocity of molecule in the X-direction
is u x. When the molecule collides with the shaded wall (see Fig. 1.1) of the
cubic box, it is reflected in the opposite direction, having a velocity of −u x
and a change of velocity of 2u x. If the distance between the shaded wall and
Depicts a particle in a cubic box of sides L colliding with the shaded
Fig. 1.1
wall.