Page 22 - Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering Ebook
P. 22
xxiii
Preface .
CH. 3. RATE LAWS AND
CH. 4 - ISOTHERMAL
REACTOR DESIGN
r I I I 1 I
I
4
CH. 7 CH 10
CH. 10
RESIDENCE
COLLECTION MULTIPLE NONELEMENTARY STEADY CATALYSIS RESIDENCE
CATALYSIS
REACTIONS 4-b HOMOGENEOUS 4-b STATE HEAT 4-b AND 4-b
AND
, - , , ~, REACTIONS EFFECTS CATALYTIC DlSTRlBtlTlON
-
-
REACTORS -
..
.
..
-
,.
4
I
CH 11
UNSTEADY EXTERNAL NONlDlEAL
NONlDlEAL
UNSTEADY
EXTERNAL
STATE HEAT DIFFUSION REACTORS
REACTORS
EFFECTS EFFECTS
EFFECTS
EFFECTS
I
A
SECTIONS
8.7 & 9.5 DIFFUSION
MULTIPLE I lNPoRoUS I
REACTIONS CATALYSTS
WITH HEAT
EFFECTS
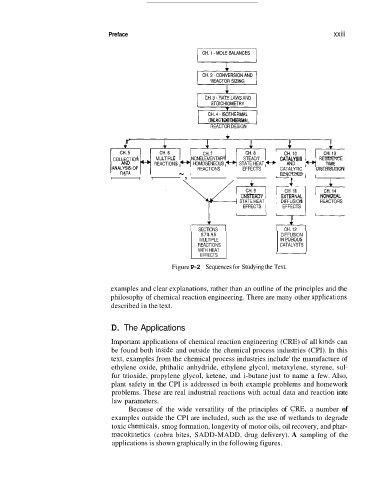
Figure P-2 Sequences for Studying the Text.
examples and clear explanations, rather than an outline of the principles and the
philosophy of chemical reaction engineering. There are many other applicatiions
described in the text.
D. The Applications
Important applications of chemical reaction engineering (CRE) of all kinds can
be found both iniside and outside the chemical process industries (CPI). In this
text, examples from the chemical process industries include' the manufacture of
ethylene oxide, phthalic anhydride, ethylene glycol, metaxylene, styrene, sul-
fur trioxide, propylene glycol, ketene, and i-butane just to name a few. Also,
plant safety in the CPI is addressed in both example problems and homework
problems. These are real industrial reactions with actual data and reaction irate
law parameters.
Because of the wide versatility of the principles of CRE, a number of
examples outside the CPI are included, such as the use of wetlands to degrade
toxic chlemicals, smog formation, longevity of motor oils, oil recovery, and phar-
macokiinetics (cobra bites, SADD-MADD, drug delivery). A sampling of the
applications is shown graphically in the following figures.