Page 336 - Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering Ebook
P. 336
See. 6.3 Algorithm for Solution to Complex Reactions 307
- TABLE E6-6.1. POLYMATH PROGRAM -
- Equations Initial Values
d(ch) /d(t) -rl+r2 0.021
d(cm) /d(t)=rl 0. 01135
d (cx) /d (t) =-rl+rZ 0
kl=55.2
k2=30.2
rlr-kl*cm* (ch**.5)
rZ=-k2*cx* (ch**.5)
tD = 0, tf = 0.5
- -
A
I
0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5
(hr)
I
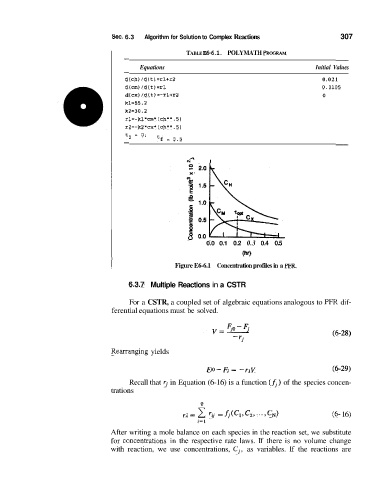
Figure E6-6.1 Concentration profiles in a PFR.
16.3.7 Multiple Reactions in a CSTR
For a CSTR, a coupled set of algebraic equations analogous to PFR dif-
ferential equations must be solved.
(16-28)
Rearranging yields
F. -F. = -r.V (6-29)
10
J
J
Recall that rj in Equation (6-16) is a function (A) of the species concen-
trations
4
r. = 1 = fj(C&? ..., CN) (6- 1 6)
'ij
J
i= 1
After writing a mole balance on each species in the reaction set, we substitute
for colncentratious in the respective rate laws. If there is no volume change
with reaction, we use concentrations, Cj, as variables. If the reactions are