Page 60 - Encyclopedia of Business and Finance
P. 60
eobf_A 7/5/06 2:54 PM Page 37
Assurance Services
audit, such as physical inspection and confirmation with engagement, the CPA applies the tools used in audits and
third parties. The review culminates in a report that pro- reviews to provide assurance on whether the subject mat-
vides limited assurance, that is, that the CPA is not aware ter of the engagement (such as internal control or manage-
of any material modifications that should be made to the ment’s discussion and analysis of operations) complies
accompanying financial statements in order for them to with applicable criteria for measurement and disclosure.
be in conformity with generally accepted accounting The result is a report much like an audit (reasonable assur-
principles. Reviews are used for quarterly financial state- ance) or review (limited assurance) of financial statements.
ments of publicly held companies. Reviews are per- In addition, CPAs can apply procedures specifically
formed for privately owned companies when the designed by the expected users of the report to financial or
financial statement user wants some assurance about the nonfinancial items. This service is neither an audit nor a
statements but do not require the level of assurance pro- review. These engagements, called agreed-upon proce-
vided in an audit. dures engagements, result in a report in which the CPA
CPAs also provide a third level of service on financial describes the procedures applied and their results but pro-
statements, the compilation. This service, provided only vides no overall conclusion.
to privately owned companies, is usually done in connec- By the 1990s CPAs were being asked to expand still
tion with helping the company record its transactions and further into additional services, including those that
transform its records into financial statements. The involve subjects far removed from financial reporting and
accountant does not do any tests of the underlying data, that do not involve an explicit report or conclusion. This
but helps put the data into financial statement form and area of service—assurance services—is an extension of
reads the statements for material misstatements. The com- the audit/attest tradition. It is generally distinct from
pilation report expresses no assurance, but if the account- common consulting services, which generally either pro-
ant discovers material misstatements, they must be vide advice to clients or create internal systems. Probably
corrected or described in the CPA’s report. the most famous assurance service is that provided in
The 1980s brought additional expansion of the CPA’s controlling and counting the ballots for the annual
role. Users wanted CPAs to use the audit and review serv- Oscars ceremony. Another common assurance service
ices to report on subjects in addition to financial state- involves CPAs observing the drawing of numbers in state
ments, such as the effectiveness of internal control and the lotteries.
company’s compliance with laws, regulations, or con- Assurance services might involve the type of reports
tracts. The profession’s response was the creation of stan- provided in more traditional attestation engagements or
dards for attestation engagements. In an attestation they might provide less structured communications, such
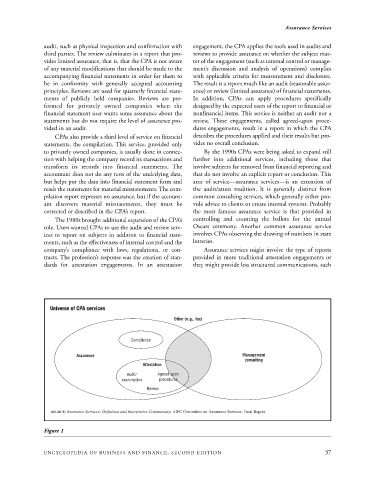
Universe of CPA services
Other (e.g., tax)
Compilation
Assurance Management
consulting
Attestation
Audit/ Agreed upon
examination procedures
Review
SOURCE: Assurance Services: Definition and Interpretive Commentary. AIPC Committee on Assurance Services. Final Report.
Figure 1
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF BUSINESS AND FINANCE, SECOND EDITION 37