Page 144 - Encyclopedia of Chemical Compounds 3 Vols
P. 144
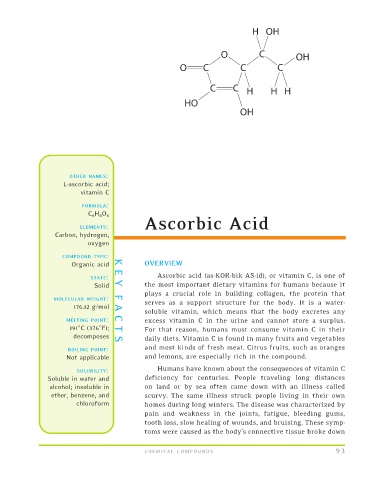
H OH
O C OH
O C C C
C C H H H
HO
OH
OTHER NAMES:
L-ascorbic acid;
vitamin C
FORMULA:
C 6 H 8 O 6
Ascorbic Acid
ELEMENTS:
Carbon, hydrogen,
oxygen
Organic acid OVERVIEW
Ascorbic acid (as-KOR-bik AS-id), or vitamin C, is one of
COMPOUND TYPE: KE
Solid the most important dietary vitamins for humans because it
STATE: Y
plays a crucial role in building collagen, the protein that
MOLECULAR WEIGHT: F
serves as a support structure for the body. It is a water-
176.12 g/mol A
soluble vitamin, which means that the body excretes any
MELTING POINT: C excess vitamin C in the urine and cannot store a surplus.
191 C (376 F); T For that reason, humans must consume vitamin C in their
decomposes S daily diets. Vitamin C is found in many fruits and vegetables
BOILING POINT: and most kinds of fresh meat. Citrus fruits, such as oranges
Not applicable and lemons, are especially rich in the compound.
SOLUBILITY: Humans have known about the consequences of vitamin C
Soluble in water and deficiency for centuries. People traveling long distances
alcohol; insoluble in on land or by sea often came down with an illness called
ether, benzene, and scurvy. The same illness struck people living in their own
chloroform homes during long winters. The disease was characterized by
pain and weakness in the joints, fatigue, bleeding gums,
tooth loss, slow healing of wounds, and bruising. These symp-
toms were caused as the body’s connective tissue broke down
CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS 93