Page 150 - Encyclopedia of Chemical Compounds 3 Vols
P. 150
H
H C H
C C
C C
H C H
H
OTHER NAMES:
Benzol;
cyclohexatriene
FORMULA:
Benzene
C 6 H 6
ELEMENTS:
Carbon, hydrogen
COMPOUND TYPE:
OVERVIEW
Aromatic hydro- KE
carbon (organic) Benzene (BEN-zeen) is a clear, colorless liquid with an
aromatic (fragrant) odor. It occurs in coal and petroleum,
STATE:
Y
from which it is extracted for commercial use. Benzene is
Liquid F
very flammable, burning with a smoking flame. The com-
MOLECULAR WEIGHT: A pound was discovered in 1825 by the English chemist and
78.11 g/mol C
physicist Michael Faraday (1791–1867), who gave the com-
MELTING POINT: T pound the name of bicarburet of hydrogen. It was given its
5.49 C (41.9 F) S modern name of benzene (benzin, at the time) by the German
chemist Eilhardt Mitscherlich (1794–1863).
BOILING POINT:
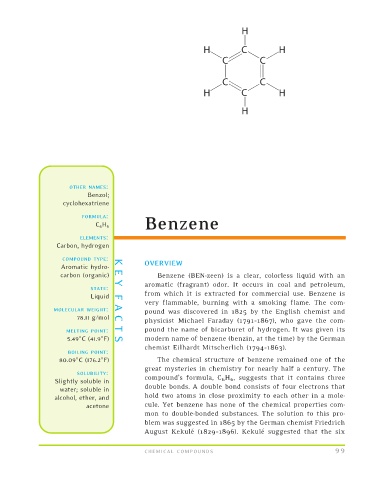
80.09 C (176.2 F) The chemical structure of benzene remained one of the
great mysteries in chemistry for nearly half a century. The
SOLUBILITY:
compound’s formula, C 6 H 6 , suggests that it contains three
Slightly soluble in
double bonds. A double bond consists of four electrons that
water; soluble in
alcohol, ether, and hold two atoms in close proximity to each other in a mole-
acetone cule. Yet benzene has none of the chemical properties com-
mon to double-bonded substances. The solution to this pro-
blem was suggested in 1865 by the German chemist Friedrich
August Kekule ´ (1829–1896). Kekule ´ suggested that the six
CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS 99