Page 66 - Encyclopedia of Chemical Compounds 3 Vols
P. 66
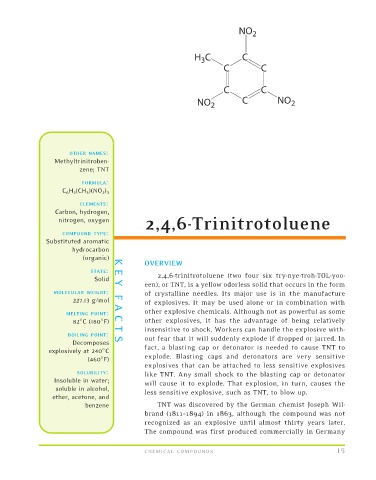
NO 2
H C C
3
C C
C C
NO 2 C NO 2
OTHER NAMES:
Methyltrinitroben-
zene; TNT
FORMULA:
C 6 H 2 (CH 3 )(NO 2 ) 3
ELEMENTS:
Carbon, hydrogen,
2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene
nitrogen, oxygen
COMPOUND TYPE:
Substituted aromatic
hydrocarbon
OVERVIEW
STATE:
2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (two four six try-nye-troh-TOL-yoo-
(organic) KE
Solid
een), or TNT, is a yellow odorless solid that occurs in the form
Y
of crystalline needles. Its major use is in the manufacture
227.13 g/mol of explosives. It may be used alone or in combination with
MOLECULAR WEIGHT: F
other explosive chemicals. Although not as powerful as some
A
82 C (180 F) other explosives, it has the advantage of being relatively
MELTING POINT: C
insensitive to shock. Workers can handle the explosive with-
T
out fear that it will suddenly explode if dropped or jarred. In
Decomposes
BOILING POINT: S
fact, a blasting cap or detonator is needed to cause TNT to
explosively at 240 C
(460 F) explode. Blasting caps and detonators are very sensitive
explosives that can be attached to less sensitive explosives
SOLUBILITY:
like TNT. Any small shock to the blasting cap or detonator
Insoluble in water;
will cause it to explode. That explosion, in turn, causes the
soluble in alcohol,
less sensitive explosive, such as TNT, to blow up.
ether, acetone, and
benzene TNT was discovered by the German chemist Joseph Wil-
brand (1811–1894) in 1863, although the compound was not
recognized as an explosive until almost thirty years later.
The compound was first produced commercially in Germany
CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS 15