Page 70 - Encyclopedia of Chemical Compounds 3 Vols
P. 70
CH
3
C
O H
N
H C H
C C
C C
H C H
OH
OTHER NAMES:
See Overview.
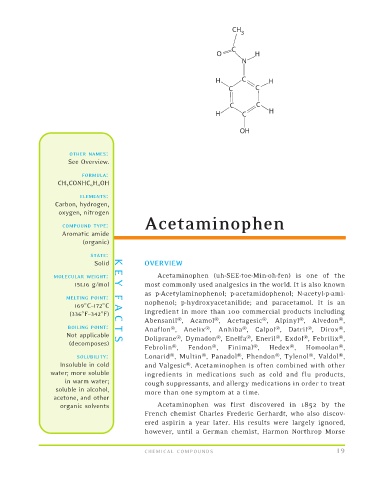
FORMULA:
CH 3 CONHC 6 H 4 OH
ELEMENTS:
Carbon, hydrogen,
oxygen, nitrogen
Acetaminophen
COMPOUND TYPE:
Aromatic amide
(organic)
STATE:
Solid KE OVERVIEW
Acetaminophen (uh-SEE-toe-Min-oh-fen) is one of the
151.16 g/mol most commonly used analgesics in the world. It is also known
MOLECULAR WEIGHT: Y
as p-Acetylaminophenol; p-acetamidophenol; N-acetyl-p-ami-
MELTING POINT: F
169 C–172 C nophenol; p-hydroxyacetanilide; and paracetamol. It is an
ingredient in more than 100 commercial products including
A
Ò
Ò
Ò
Ò
Ò
Abensanil , Acamol , Acetagesic , Alpinyl , Alvedon ,
(336 F–342 F) C
BOILING POINT: T Anaflon , Anelix , Anhiba , Calpol , Datril , Dirox ,
Ò
Ò
Ò
Ò
Ò
Ò
Ò
Ò
Ò
Ò
Ò
Ò
Doliprane , Dymadon , Enelfa , Eneril , Exdol , Febrilix ,
(decomposes)
Not applicable S
Ò
Ò
Ò
Ò
Ò
Febrolin , Fendon , Finimal , Hedex , Homoolan ,
Ò
Ò
Ò
Ò
Ò
Ò
SOLUBILITY: Lonarid , Multin , Panadol , Phendon , Tylenol , Valdol ,
Insoluble in cold and Valgesic . Acetaminophen is often combined with other
Ò
water; more soluble ingredients in medications such as cold and flu products,
in warm water; cough suppressants, and allergy medications in order to treat
soluble in alcohol,
more than one symptom at a time.
acetone, and other
organic solvents Acetaminophen was first discovered in 1852 by the
French chemist Charles Frederic Gerhardt, who also discov-
ered aspirin a year later. His results were largely ignored,
however, until a German chemist, Harmon Northrop Morse
CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS 19