Page 88 - Encyclopedia of Chemical Compounds 3 Vols
P. 88
CH 3
H H C CH 3
CH H C C H
3
H H C C H H
H CH H C C H H
3
CH
3 H
H H C C H
HO C C H
C C C H C C H H
H
H H H
C C C C
H C C O CH H
3 3
CH 3
OTHER NAMES:
See Overview.
FORMULA:
C 29 H 50 O
ELEMENTS:
Carbon, hydrogen, Alpha-Tocopherol
oxygen
COMPOUND TYPE:
Organic
STATE: KE OVERVIEW
Liquid
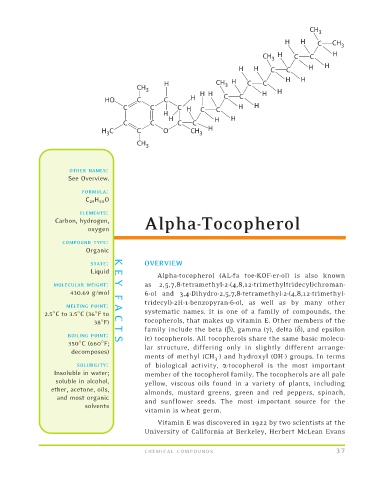
Alpha-tocopherol (AL-fa toe-KOF-er-ol) is also known
MOLECULAR WEIGHT: Y as 2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)chroman-
6-ol and 3,4-Dihydro-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyl-
430.69 g/mol F
tridecyl)-2H-1-benzopyran-6-ol, as well as by many other
MELTING POINT: A
systematic names. It is one of a family of compounds, the
tocopherols, that makes up vitamin E. Other members of the
2.5 Cto3.5 C(36 Fto C
family include the beta (b), gamma (g), delta (d), and epsilon
38 F) T
(E) tocopherols. All tocopherols share the same basic molecu-
350 C (660 F;
BOILING POINT: S
lar structure, differing only in slightly different arrange-
decomposes)
ments of methyl (CH 3 -) and hydroxyl (OH-) groups. In terms
SOLUBILITY: of biological activity, a-tocopherol is the most important
Insoluble in water; member of the tocopherol family. The tocopherols are all pale
soluble in alcohol, yellow, viscous oils found in a variety of plants, including
ether, acetone, oils,
almonds, mustard greens, green and red peppers, spinach,
and most organic
and sunflower seeds. The most important source for the
solvents
vitamin is wheat germ.
Vitamin E was discovered in 1922 by two scientists at the
University of California at Berkeley, Herbert McLean Evans
CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS 37