Page 223 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioTechnology
P. 223
P1: ZBU Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN011J-141 July 31, 2001 15:14
800 Pharmaceuticals, Controlled Release of
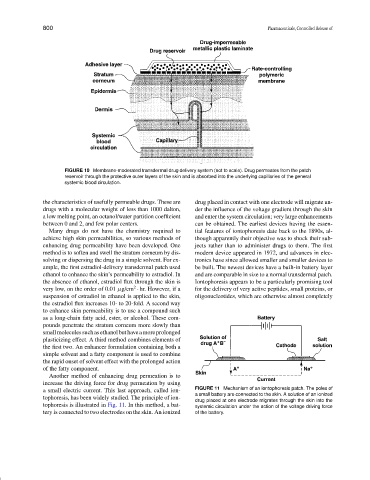
FIGURE 10 Membrane-moderated transdermal drug delivery system (not to scale). Drug permeates from the patch
reservoir through the protective outer layers of the skin and is absorbed into the underlying capillaries of the general
systemic blood circulation.
the characteristics of usefully permeable drugs. These are drug placed in contact with one electrode will migrate un-
drugs with a molecular weight of less than 1000 dalton, der the influence of the voltage gradient through the skin
a low melting point, an octanol/water partition coefficient and enter the system circulation; very large enhancements
between 0 and 2, and few polar centers. can be obtained. The earliest devices having the essen-
Many drugs do not have the chemistry required to tial features of iontophoresis date back to the 1890s, al-
achieve high skin permeabilities, so various methods of though apparently their objective was to shock their sub-
enhancing drug permeability have been developed. One jects rather than to administer drugs to them. The first
method is to soften and swell the stratum corneum by dis- modern device appeared in 1972, and advances in elec-
solving or dispersing the drug in a simple solvent. For ex- tronics have since allowed smaller and smaller devices to
ample, the first estradiol-delivery transdermal patch used be built. The newest devices have a built-in battery layer
ethanol to enhance the skin’s permeability to estradiol. In and are comparable in size to a normal transdermal patch.
the absence of ethanol, estradiol flux through the skin is Iontophoresis appears to be a particularly promising tool
2
very low, on the order of 0.01 µg/cm · hr. However, if a for the delivery of very active peptides, small proteins, or
suspension of estradiol in ethanol is applied to the skin, oligonucleotides, which are otherwise almost completely
the estradiol flux increases 10- to 20-fold. A second way
to enhance skin permeability is to use a compound such
as a long-chain fatty acid, ester, or alcohol. These com-
pounds penetrate the stratum corneum more slowly than
smallmoleculessuchasethanolbuthaveamoreprolonged
plasticizing effect. A third method combines elements of
the first two. An enhancer formulation containing both a
simple solvent and a fatty component is used to combine
the rapid onset of solvent effect with the prolonged action
of the fatty component.
Another method of enhancing drug permeation is to
increase the driving force for drug permeation by using
a small electric current. This last approach, called ion- FIGURE 11 Mechanism of an iontophoresis patch. The poles of
a small battery are connected to the skin. A solution of an ionized
tophoresis, has been widely studied. The principle of ion-
drug placed at one electrode migrates through the skin into the
tophoresis is illustrated in Fig. 11. In this method, a bat- systemic circulation under the action of the voltage driving force
tery is connected to two electrodes on the skin. An ionized of the battery.