Page 395 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Chemical Engineering
P. 395
P1: GLQ Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN009K-419 July 19, 2001 20:57
330 Membranes, Synthetic, Applications
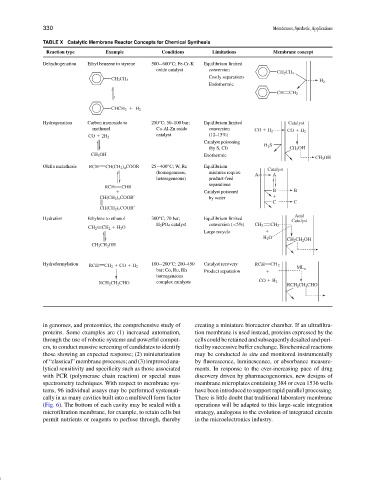
TABLE X Catalytic Membrane Reactor Concepts for Chemical Synthesis
Reaction type Example Conditions Limitations Membrane concept
◦
Dehydrogenation Ethyl benzene to styrene 500−600 C; Fe-Cr-K Equilibrium limited
oxide catalyst conversion
CH 2 CH 3
Costly separations
CH 2 CH 3
H 2
Endothermic
CH CH 2
CHCH 2 H 2
◦
Hydrogenation Carbon monoxide to 250 C; 50–100 bar; Equilibrium limited Catalyst
methanol Cu-Al-Zn oxide conversion
CO H 2 CO H 2
catalyst (12–15%)
CO 2H 2
Catalyst poisoning H 2 S
(by S, Cl) CH 3 OH
CH 3 OH Exothermic
CH 3 OH
◦
Olefin metathesis RCH CH(CH 2 ) n COOR 25−400 C; W, Re Equilibrium Catalyst
(homogeneous, mixtures require A A
heterogeneous) product-feed
separations
RCH CHR
Catalyst poisoned B B
CH(CH 2 ) n COOR′ by water
C C
CH(CH 2 ) n COOR′
Acid
◦
Hydration Ethylene to ethanol 300 C; 70 bar; Equilibrium limited
Catalyst
H 2 PO 4 catalyst conversion (<5%)
CH 2 H 2 O CH 2 CH 2
CH 2
Large recycle
H 2 O
CH 2 CH 2 OH
CH 3 CH 2 OH
◦
Hydroformylation RCH CH 2 CO H 2 100−200 C; 200–450 Catalyst recovery RCH CH 2
bar; Co, Ru, Rh Product separation ML n
homogeneous
RCH 2 CH 2 CHO complex catalysts CO H 2
RCH 2 CH 2 CHO
in genomes, and proteomics, the comprehensive study of creating a miniature bioreactor chamber. If an ultrafiltra-
proteins. Some examples are (1) increased automation, tion membrane is used instead, proteins expressed by the
through the use of robotic systems and powerful comput- cells could be retained and subsequently desalted and puri-
ers, to conduct massive screening of candidates to identify fied by successive buffer exchange. Biochemical reactions
those showing an expected response; (2) miniaturization may be conducted in situ and monitored instrumentally
of “classical” membrane processes; and (3) improved ana- by fluorescence, luminescence, or absorbance measure-
lytical sensitivity and specificity such as those associated ments. In response to the ever-increasing pace of drug
with PCR (polymerase chain reaction) or special mass discovery driven by pharmacogenomics, new designs of
spectrometry techniques. With respect to membrane sys- membrane microplates containing 384 or even 1536 wells
tems, 96 individual assays may be performed systemati- have been introduced to support rapid parallel processing.
cally in as many cavities built into a multiwell form factor There is little doubt that traditional laboratory membrane
(Fig. 6). The bottom of each cavity may be sealed with a operations will be adapted to this large-scale integration
microfiltration membrane, for example, to retain cells but strategy, analogous to the evolution of integrated circuits
permit nutrients or reagents to perfuse through, thereby in the microelectronics industry.