Page 451 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Chemical Engineering
P. 451
P1: GPB/GAM P2: GQT Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN013A-619 July 26, 2001 19:32
256 Pulp and Paper
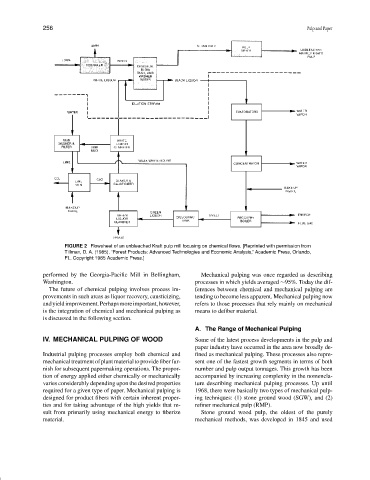
FIGURE 2 Flowsheet of an unbleached Kraft pulp mill focusing on chemical flows. [Reprinted with permission from
Tillman, D. A. (1985). “Forest Products: Advanced Technologies and Economic Analysis,” Academic Press, Orlando,
FL. Copyright 1985 Academic Press.]
performed by the Georgia-Pacific Mill in Bellingham, Mechanical pulping was once regarded as describing
Washington. processes in which yields averaged ∼95%. Today the dif-
The future of chemical pulping involves process im- ferences between chemical and mechanical pulping are
provements in such areas as liquor recovery, causticizing, tending to become less apparent. Mechanical pulping now
andyieldimprovement.Perhapsmoreimportant,however, refers to those processes that rely mainly on mechanical
is the integration of chemical and mechanical pulping as means to defiber material.
is discussed in the following section.
A. The Range of Mechanical Pulping
IV. MECHANICAL PULPING OF WOOD Some of the latest process developments in the pulp and
paper industry have occurred in the area now broadly de-
Industrial pulping processes employ both chemical and fined as mechanical pulping. These processes also repre-
mechanical treatment of plant material to provide fiber fur- sent one of the fastest growth segments in terms of both
nish for subsequent papermaking operations. The propor- number and pulp output tonnages. This growth has been
tion of energy applied either chemically or mechanically accompanied by increasing complexity in the nomencla-
varies considerably depending upon the desired properties ture describing mechanical pulping processes. Up until
required for a given type of paper. Mechanical pulping is 1968, there were basically two types of mechanical pulp-
designed for product fibers with certain inherent proper- ing techniques: (1) stone ground wood (SGW), and (2)
ties and for taking advantage of the high yields that re- refiner mechanical pulp (RMP).
sult from primarily using mechanical energy to fiberize Stone ground wood pulp, the oldest of the purely
material. mechanical methods, was developed in 1845 and used