Page 463 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Chemical Engineering
P. 463
P1: GNH/GUR P2: GPJ Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN014A-654 July 28, 2001 16:35
Reactors in Process Engineering 25
a. Gas–liquid
b. Gas–solid
c. Liquid–solid
d. Gas–liquid–solid
Multiphase reactor configurations are strongly influenced
by mass transfer operations. Any of the reactor types pre-
sented above can be operated as multiphase reactors.
C. Reaction Types
Classification of reactors can also be made by reaction
type.
1. Catalytic. Reactions that require the presence of a
catalyst to obtain the rate conditions necessary for
that particular reactor design
2. Noncatalytic. Reactions that do not include either a
homogeneous or heterogeneous catalyst
3. Autocatalytic. Reaction scheme whereby one of the
products increases the overall rate of reaction
4. Biological. Reactions that involve living cells
(enzymes, bacteria, or yeast), parts of cells, or
products from cells required for the reaction
scheme
5. Polymerization. Reactions that involve formation of
molecular chains, whether on a solid support or in
solution.
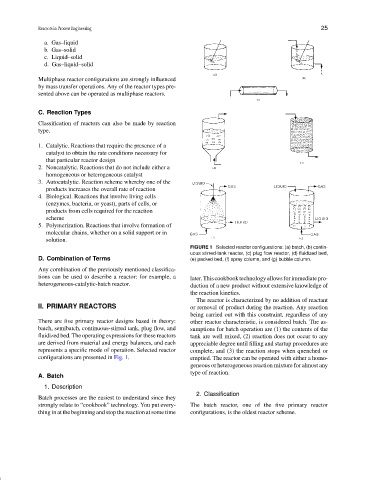
FIGURE 1 Selected reactor configurations: (a) batch, (b) contin-
uous stirred-tank reactor, (c) plug flow reactor, (d) fluidized bed,
D. Combination of Terms (e) packed bed, (f) spray column, and (g) bubble column.
Any combination of the previously mentioned classifica-
tions can be used to describe a reactor: for example, a later.Thiscookbooktechnologyallowsforimmediatepro-
heterogeneous-catalytic-batch reactor. duction of a new product without extensive knowledge of
the reaction kinetics.
The reactor is characterized by no addition of reactant
II. PRIMARY REACTORS or removal of product during the reaction. Any reaction
being carried out with this constraint, regardless of any
There are five primary reactor designs based in theory: other reactor characteristic, is considered batch. The as-
batch, semibatch, continuous-stirred tank, plug flow, and sumptions for batch operation are (1) the contents of the
fluidized bed. The operating expressions for these reactors tank are well mixed, (2) reaction does not occur to any
are derived from material and energy balances, and each appreciable degree until filling and startup procedures are
represents a specific mode of operation. Selected reactor complete, and (3) the reaction stops when quenched or
configurations are presented in Fig. 1. emptied. The reactor can be operated with either a homo-
geneous or heterogeneous reaction mixture for almost any
type of reaction.
A. Batch
1. Description
2. Classification
Batch processes are the easiest to understand since they
strongly relate to “cookbook” technology. You put every- The batch reactor, one of the five primary reactor
thing in at the beginning and stop the reaction at some time configurations, is the oldest reactor scheme.