Page 267 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Organic Chemistry
P. 267
P1: LDK/GJK P2: GQT/Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN012G-576 July 28, 2001 12:44
Physical Organic Chemistry 213
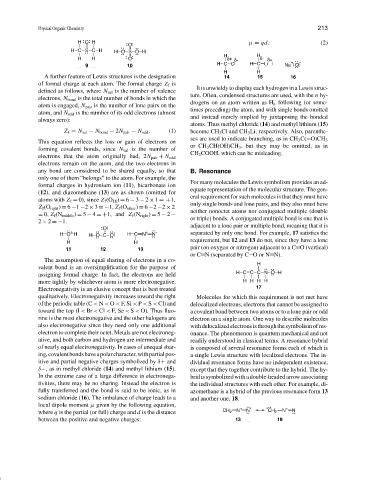
µ = qd. (2)
A further feature of Lewis structures is the designation
of formal charge at each atom. The formal charge Z f is
It is unwieldy to display each hydrogen in a Lewis struc-
defined as follows, where N val is the number of valence
ture. Often, condensed structures are used, with the n hy-
electrons, N bond is the total number of bonds in which the
drogens on an atom written as H n following (or some-
atom is engaged, N pair is the number of lone pairs on the
times preceding) the atom, and with single bonds omitted
atom, and N odd is the number of its odd electrons (almost
and instead merely implied by juxtaposing the bonded
always zero):
atoms. Thus methyl chloride (14) and methyl lithium (15)
Z f = N val − N bond − 2N pair − N odd . (1) become CH 3 Cl and CH 3 Li, respectively. Also, parenthe-
This equation reflects the loss or gain of electrons on ses are used to indicate branching, as in CH 3 C( O)CH 3
or CH 3 CH(OH)CH 3 , but they may be omitted, as in
forming covalent bonds, since N val is the number of
CH 3 COOH, which can be misleading.
electrons that the atom originally had, 2N pair + N odd
electrons remain on the atom, and the two electrons in
any bond are considered to be shared equally, so that B. Resonance
only one of them “belongs” to the atom. For example, the
For many molecules the Lewis symbolism provides an ad-
formal charges in hydronium ion (11), bicarbonate ion
equate representation of the molecular structure. The gen-
(12), and diazomethane (13) are as shown (omitted for
eral requirement for such molecules is that they must have
atoms with Z f = 0), since Z f (O 11 ) = 6 − 3 − 2 × 1 =+1,
only single bonds and lone pairs, and they also must have
Z f (O right ) = 6 −1 −2 × 3 =−1, Z f (O other ) = 6 −2 −2 × 2
neither nonoctet atoms nor conjugated multiple (double
= 0, Z f (N middle ) = 5 − 4 =+1, and Z f (N right ) = 5 − 2 −
or triple) bonds. A conjugated multiple bond is one that is
2 × 2 =−1.
adjacent to a lone pair or multiple bond, meaning that it is
separated by only one bond. For example, 17 satisfies the
requirement, but 12 and 13 do not, since they have a lone
pair (on oxygen or nitrogen) adjacent to a C O (vertical)
or C N (separated by C OorN N).
The assumption of equal sharing of electrons in a co-
valent bond is an oversimplification for the purpose of
assigning formal charge. In fact, the electrons are held
more tightly by whichever atom is more electronegative.
Electronegativity is an elusive concept that is best treated
qualitatively. Electronegativity increases toward the right Molecules for which this requirement is not met have
of the periodic table (C < N < O < F, Si < P < S < Cl) and delocalized electrons, electrons that cannot be assigned to
toward the top (I < Br < Cl < F, Se < S < O). Thus fluo- a covalent bond between two atoms or to a lone pair or odd
rine is the most electronegative and the other halogens are electron on a single atom. One way to describe molecules
also electronegative since they need only one additional withdelocalizedelectronsisthroughthesymbolismofres-
electron to complete their octet. Metals are not electroneg- onance. The phenomenon is quantum mechanical and not
ative, and both carbon and hydrogen are intermediate and readily understood in classical terms. A resonance hybrid
of nearly equal electronegativity. In cases of unequal shar- is composed of several resonance forms each of which is
ing,covalentbondshaveapolarcharacter,withpartialpos- a single Lewis structure with localized electrons. The in-
itive and partial negative charges symbolized by δ+ and dividual resonance forms have no independent existence,
δ−, as in methyl chloride (14) and methyl lithium (15). except that they together contribute to the hybrid. The hy-
In the extreme case of a large difference in electronega- brid is symbolized with a double-headed arrow associating
tivities, there may be no sharing. Instead the electron is the individual structures with each other. For example, di-
fully transferred and the bond is said to be ionic, as in azomethane is a hybrid of the previous resonance form 13
sodium chloride (16). The imbalance of charge leads to a and another one, 18.
local dipole moment µ given by the following equation,
where q is the partial (or full) charge and d is the distance
between the positive and negative charges: