Page 279 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Organic Chemistry
P. 279
P1: LDK/GJK P2: GQT/Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN012G-576 July 28, 2001 12:44
Physical Organic Chemistry 225
an electrostatic effect. The energy of interaction of two
point charges q 1 and q 2 with each other or of one point
charge with a dipole moment µ [Eq. (2)] is given as fol-
lows, where r is the distance between the two, ε is the
dielectric constant of the solvent, and θ is the angle be-
tween the direction of the dipole and the direction toward
the charge:
q 1 q 2
E charge-charge = , (25)
εr
q µ cos θ
E charge-dipole = . (26)
εr 2
These correspond to an energy lowering when two op-
posite charges are near each other or when the charge is
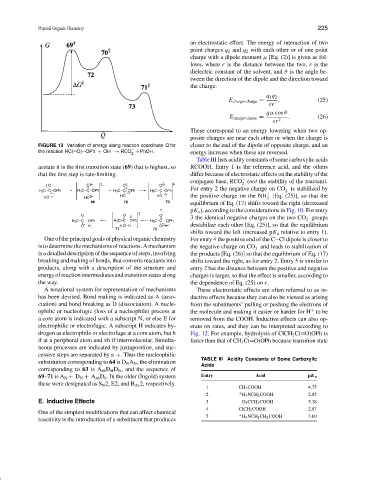
FIGURE 13 Variation of energy along reaction coordinate Q for closer to the end of the dipole of opposite charge, and an
−
the reaction RC( O) OPh + OH → RCO + PhOH. energy increase when these are reversed.
−
2
Table III lists acidity constants of some carboxylic acids
acetate it is the first transition state (69) that is highest, so RCOOH. Entry 1 is the reference acid, and the others
that the first step is rate-limiting. differ because of electrostatic effects on the stability of the
conjugate base, RCO (not the stability of the reactant).
−
2
−
For entry 2 the negative charge on CO is stabilized by
2
+
the positive charge on the NH [Eq. (25)], so that the
3
equilibrium of Eq. (17) shifts toward the right (decreased
pK a ), according to the considerations in Fig. 10. For entry
−
3 the identical negative charges on the two CO groups
2
destabilize each other [Eq. (25)], so that the equilibrium
shifts toward the left (increased pK a relative to entry 1).
One of the principal goals of physical organic chemistry For entry 4 the positive end of the C Cl dipole is closer to
is to determine the mechanisms of reactions. A mechanism the negative charge on CO and leads to stabilization of
−
2
is a detailed description of the sequence of steps, involving the products [Eq. (26)] so that the equilibrium of Eq. (17)
breaking and making of bonds, that converts reactants into shifts toward the right, as for entry 2. Entry 5 is similar to
products, along with a description of the structure and entry 2 but the distance between the positive and negative
energyofreactionintermediatesandtransitionstatesalong charges is larger, so that the effect is smaller, according to
the way. the dependence of Eq. (25) on r.
A notational system for representation of mechanisms These electrostatic effects are often referred to as in-
has been devised. Bond making is indicated as A (asso- ductive effects because they can also be viewed as arising
ciation) and bond breaking as D (dissociation). A nucle- from the substituents’ pulling or pushing the electrons of
+
ophilic or nucleofugic (loss of a nucleophile) process at the molecule and making it easier or harder for H to be
a core atom is indicated with a subscript N, or else E for removed from the COOH. Inductive effects can also op-
electrophilic or electrofugic. A subscript H indicates hy- erate on rates, and they can be interpreted according to
drogen as electrophile or electrofuge at a core atom, but h Fig. 12. For example, hydrolysis of ClCH 2 C( O)OPh is
if at a peripheral atom and xh if intermolecular. Simulta- faster than that of CH 3 C( O)OPh because transition state
neous processes are indicated by juxtaposition, and suc-
cessive steps are separated by a +. Thus the nucleophilic
TABLE III Acidity Constants of Some Carboxylic
substitution corresponding to 64 is D N A N , the elimination
Acids
corresponding to 63 is A xh D H D N , and the sequence of
69–71 is A N + D N + A xh D h . In the older (Ingold) system Entry Acid pK a
these were designated as S N 2, E2, and B Ac 2, respectively.
1 CH 3 COOH 4.75
2 + H 3 NCH 2 COOH 2.85
E. Inductive Effects 3 − O 2 CCH 2 COOH 5.38
4 ClCH 2 COOH 2.87
One of the simplest modifications that can affect chemical
5 + H 3 NCH 2 CH 2 COOH 3.60
reactivity is the introduction of a substituent that produces