Page 58 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Organic Chemistry
P. 58
P1: ZCK 2nd Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002G-51 May 25, 2001 13:44
96 Bioconjugate Chemistry
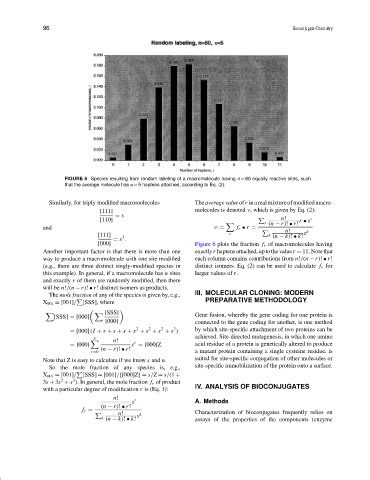
FIGURE 6 Species resulting from random labeling of a macromolecule having n = 60 equally reactive sites, such
that the average molecule has n = 5 haptens attached, according to Eq. (2).
Similarly, for triply modified macromolecules Theaveragevalueofr inarealmixtureofmodifiedmacro-
[111] molecules is denoted ν, which is given by Eq. (2):
= s
[110] n! r • s r
r
(n − r)! • r!
and υ = f r • r =
n! k
[111] 3 r k (n − k)! • k! s
= s .
[000] Figure 6 plots the fraction f r of macromolecules having
Another important factor is that there is more than one exactlyr haptensattached,uptothevaluer = 11.Notethat
way to produce a macromolecule with one site modified each column contains contributions from n!/(n −r)! • r!
(e.g., there are three distinct singly-modified species in distinct isomers. Eq. (2) can be used to calculate f r for
this example). In general, if a macromolecule has n sites larger values of r.
and exactly r of them are randomly modified, then there
will be n!/(n −r)! • r! distinct isomers as products.
The mole fraction of any of the species is given by, e.g., III. MOLECULAR CLONING: MODERN
PREPARATIVE METHODOLOGY
X 001 = [001]/ [SSS], where
[SSS]
[SSS] = [000] Gene fusion, whereby the gene coding for one protein is
[000] connected to the gene coding for another, is one method
2
2
2
3
= [000] (I + s + s + s + s + s + s + s ) by which site-specific attachment of two proteins can be
achieved. Site-directed mutagenesis, in which one amino
n
n! r
= [000] s = [000]Z acid residue of a protein is genetically altered to produce
(n − r)! • r!
r=0 a mutant protein containing a single cysteine residue, is
Note that Z is easy to calculate if we know s and n. suited for site-specific conjugation of other molecules or
So the mole fraction of any species is, e.g., site-specific immobilization of the protein onto a surface.
X 001 = [001]/ [SSS] = [001]/{[000]Z}= s/Z = s/(1 +
2
3
3s + 3s + s ). In general, the mole fraction f r of product
IV. ANALYSIS OF BIOCONJUGATES
with a particular degree of modification r is (Eq. 1):
n! r
s A. Methods
(n − r)! • r!
f r =
n! k Characterization of bioconjugates frequently relies on
k (n − k)! • k! s assays of the properties of the components (enzyme