Page 158 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Analytical Chemistry
P. 158
P1: LLL/LPB P2: FJU Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN005F220 June 15, 2001 20:44
400 Elemental Analysis, Organic Compounds
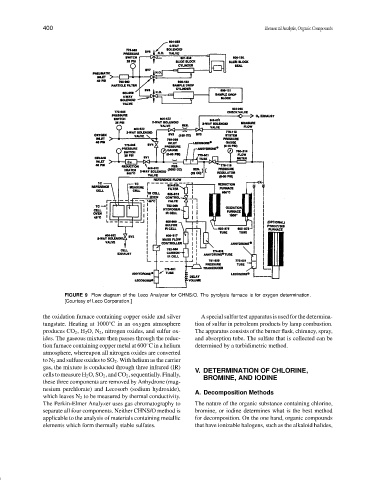
FIGURE 9 Flow diagram of the Leco Analyzer for CHNS/O. The pyrolysis furnace is for oxygen determination.
[Courtesy of Leco Corporation.]
the oxidation furnace containing copper oxide and silver A special sulfur test apparatus is used for the determina-
tungstate. Heating at 1000 C in an oxygen atmosphere tion of sulfur in petroleum products by lamp combustion.
◦
produces CO 2 ,H 2 O, N 2 , nitrogen oxides, and sulfur ox- The apparatus consists of the burner flask, chimney, spray,
ides. The gaseous mixture then passes through the reduc- and absorption tube. The sulfate that is collected can be
◦
tion furnace containing copper metal at 600 C in a helium determined by a turbidimetric method.
atmosphere, whereupon all nitrogen oxides are converted
to N 2 and sulfure oxides to SO 2 . With helium as the carrier
gas, the mixture is conducted through three infrared (IR) V. DETERMINATION OF CHLORINE,
cells to measure H 2 O, SO 2 , and CO 2 , sequentially. Finally, BROMINE, AND IODINE
these three components are removed by Anhydrone (mag-
nesium perchlorate) and Lecosorb (sodium hydroxide),
A. Decomposition Methods
which leaves N 2 to be measured by thermal conductivity.
The Perkin-Elmer Analyzer uses gas chromatography to The nature of the organic substance containing chlorine,
separate all four components. Neither CHNS/O method is bromine, or iodine determines what is the best method
applicable to the analysis of materials containing metallic for decomposition. On the one hand, organic compounds
elements which form thermally stable sulfates. that have ionizable halogens, such as the alkaloid halides,