Page 333 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Analytical Chemistry
P. 333
P1: GNH Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN009N-447 July 19, 2001 23:3
850 Microwave Molecular Spectroscopy
time-domain signal is converted to the frequency domain signal) computed from the time-domain signal to give
by calculating the Fourier transform. Earlier waveguide the spectrum. Because the cavity is tuned to ν and has
MWFT spectrometers developed by Drizler and cowork- a very narrow bandwidth (∼1 MHz), a high radiation den-
ers used square cross-section sample cells. Improved ver- sity is obtained. This produces appreciable polarization
sions have used circular waveguide sample cells and of the complex when rotational transitions lie inside the
bridge-type arrangements where one arm of the bridge frequency bandwidth. Switch 2 serves to protect the de-
is the sample cell and the other arm the reference cell. tector, and its opening is delayed to allow the microwave
In the study of complexes, a Fabry-Perot cavity is em- pulse to dissipate within the cavity before detection of the
ployed as a sample cell along with a pulsed supersonic weak, longer duration, coherent resonant rotational emis-
nozzle source. The weakly bonded complex is produced sion. Gas pulses are repeated by rapid evacuation of the
at very low temperatures (a few degrees Kelvin), by ex- cavity at a rate of ∼1 per second. A timing scheme is set
panding (adiabatically) as a short pulse a mixture of the up to properly sequence the various events and to allow
reactive species in an inert buffer gas. Weak complex for- alternate collection of the background which is subtracted
mation occurs undoubtedly via three-body collisions, for from the molecular emission. Various cycles are averaged
example, to produce the desired spectrum.
Though the resolution is exceptionally higher, because
Xe + Xe + HCl → Xe···HCl + Xe,
of the narrow bandwidth, only small elements of the spec-
and the low temperatures obtained help stabilize the tra can be covered at a time. Also, the low gas temperature
complex. allows primarily the ground vibrational state to be studied.
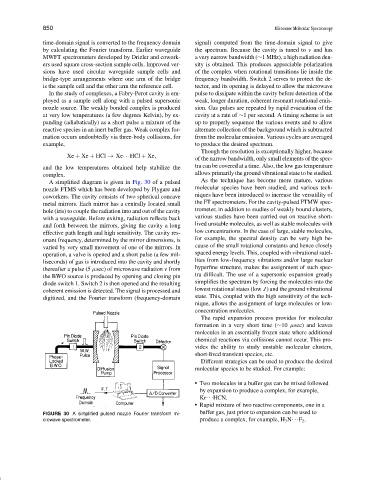
A simplified diagram is given in Fig. 30 of a pulsed As the technique has become more mature, various
nozzle FTMS which has been developed by Flygare and molecular species have been studied, and various tech-
coworkers. The cavity consists of two spherical concave niques have been introduced to increase the versatility of
metal mirrors. Each mirror has a centrally located small the FT spectrometers. For the cavity-pulsed FTMW spec-
hole (iris) to couple the radiation into and out of the cavity trometer, in addition to studies of weakly bound clusters,
with a waveguide. Before exiting, radiation reflects back various studies have been carried out on reactive short-
and forth between the mirrors, giving the cavity a long lived unstable molecules, as well as stable molecules with
effective path length and high sensitivity. The cavity res- low concentrations. In the case of large, stable molecules,
onant frequency, determined by the mirror dimensions, is for example, the spectral density can be very high be-
varied by very small movement of one of the mirrors. In cause of the small rotational constants and hence closely
operation, a valve is opened and a short pulse (a few mil- spaced energy levels. This, coupled with vibrational satel-
liseconds) of gas is introduced into the cavity and shortly lites from low-frequency vibrations and/or large nuclear
thereafter a pulse (5 µsec) of microwave radiation ν from hyperfine structure, makes the assignment of such spec-
the BWO source is produced by opening and closing pin tra difficult. The use of a supersonic expansion greatly
diode switch 1. Switch 2 is then opened and the resulting simplifies the spectrum by forcing the molecules into the
coherent emission is detected. The signal is processed and lowest rotational states (low J) and the ground vibrational
digitized, and the Fourier transform (frequency-domain state. This, coupled with the high sensitivity of the tech-
nique, allows the assignment of large molecules or low-
concentration molecules.
The rapid expansion process provides for molecular
formation in a very short time (∼10 µsec) and leaves
molecules in an essentially frozen state where additional
chemical reactions via collisions cannot occur. This pro-
vides the ability to study unstable molecular clusters,
short-lived transient species, etc.
Different strategies can be used to produce the desired
molecular species to be studied. For example:
Two molecules in a buffer gas can be mixed followed
by expansion to produce a complex, for example,
Kr···HCN.
Rapid mixture of two reactive components, one in a
FIGURE 30 A simplified pulsed nozzle Fourier transform mi- buffer gas, just prior to expansion can be used to
crowave spectrometer. produce a complex, for example, H 3 N···F 2 .