Page 360 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Analytical Chemistry
P. 360
P1: LLL/LOS/GJM P2: GLM Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN0011A-541 July 25, 2001 17:27
Organic Chemistry, Compound Detection 463
detector in GC can readily detect 10 −11 g and the electron
capture detector can detect 10 −10 –10 −12 gofmanyor-
ganic compounds. The refractive index detector in liquid
chromatography is limited to about 10 −6 g; the ultraviolet
(UV) detector can detect 10 −8 g for many highly conju-
gated compounds. The resolution efficiency of a column is
expressed in “theoretical plates.” Thus, packed gas chro-
matographic columns of reasonable lengths can generate
2000–10,000 plates. Open tabular column (capillary size
columns) can easily generate 50,000–100,000 plates. To-
tal plates available in LC is greatly affected by pressure
and analysis time available. Assuming 5,000 psi and flow
rates of 0.5 ml/min, a reasonable upper limit is 10,000
plates.
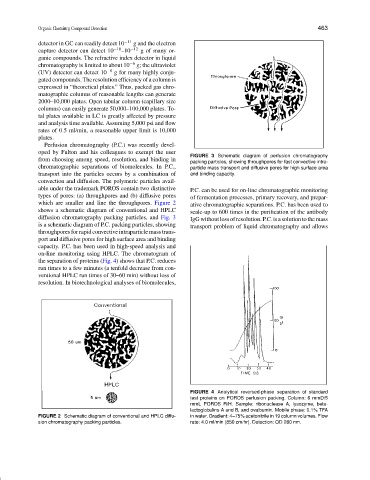
Perfusion chromatography (P.C.) was recently devel-
oped by Fulton and his colleagues to exempt the user
FIGURE 3 Schematic diagram of perfusion chromatography
from choosing among speed, resolution, and binding in
packing particles, showing throughpores for fast convective intra-
chromatographic separations of biomolecules. In P.C., particle mass transport and diffusive pores for high surface area
transport into the particles occurs by a combination of and binding capacity.
convection and diffusion. The polymeric particles avail-
able under the trademark POROS contain two distinctive P.C. can be used for on-line chromatographic monitoring
types of pores: (a) throughpores and (b) diffusive pores of fermentation processes, primary recovery, and prepar-
which are smaller and line the throughpores. Figure 2 ative chromatographic separations. P.C. has been used to
shows a schematic diagram of conventional and HPLC scale-up to 600 times in the purification of the antibody
diffusion chromatography packing particles, and Fig. 3 IgGwithoutlossofresolution.P.C.isasolutiontothemass
is a schematic diagram of P.C. packing particles, showing transport problem of liquid chromatography and allows
throughpores for rapid convective intraparticle mass trans-
port and diffusive pores for high surface area and binding
capacity. P.C. has been used in high-speed analysis and
on-line monitoring using HPLC. The chromatogram of
the separation of proteins (Fig. 4) shows that P.C. reduces
run times to a few minutes (a tenfold decrease from con-
ventional HPLC run times of 30–60 min) without loss of
resolution. In biotechnological analyses of biomolecules,
FIGURE 4 Analytical reversed-phase separation of standard
test proteins on POROS perfusion packing. Column: 6 mmD/5
mmL POROS R/H. Sample: ribonuclease A, lysozyme, beta-
lactoglobulins A and B, and ovalbumin. Mobile phase: 0.1% TFA
FIGURE 2 Schematic diagram of conventional and HPLC diffu- in water. Gradient: 4–75% acetonitrile in 19 column volumes. Flow
sion chromatography packing particles. rate: 4.0 ml/min (850 cm/hr). Detection: OD 280 nm.