Page 359 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Analytical Chemistry
P. 359
P1: LLL/LOS/GJM P2: GLM Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN0011A-541 July 25, 2001 17:27
462 Organic Chemistry, Compound Detection
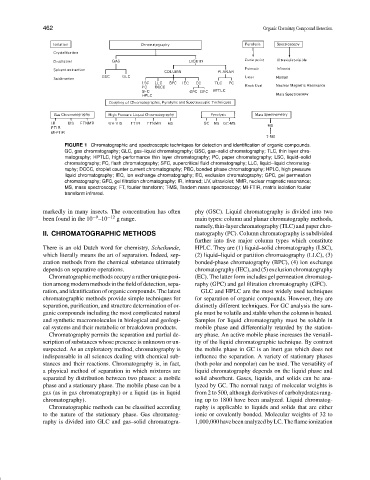
FIGURE 1 Chromatographic and spectroscopic techniques for detection and identification of organic compounds.
GC, gas chromatography; GLC, gas–liquid chromatography; GSC, gas–solid chromatography; TLC, thin layer chro-
matography; HPTLC, high-performance thin layer chromatography; PC, paper chromatography; LSC, liquid–solid
chromatography; FC, flash chromatography; SFC, supercritical fluid chromatography; LLC, liquid–liquid chromatog-
raphy; DCCC, droplet counter current chromatography; PBC, bonded phase chromatography; HPLC, high pressure
liquid chromatography; IEC, ion exchange chromatography; EC, exclusion chromatography; GPC, gel permeation
chromatography; GFC, gel filtration chromatography; IR, infrared; UV, ultraviolet; NMR, nuclear magnetic resonance;
MS, mass spectroscopy; FT, fourier transform; T-MS, Tandem mass spectroscopy; MI-FTIR, matrix isolation fourier
transform infrared.
markedly in many insects. The concentration has often phy (GSC). Liquid chromatography is divided into two
−9
been found in the 10 –10 −12 g range. main types: column and planar chromatography methods,
namely, thin-layer chromatography (TLC) and paper chro-
II. CHROMATOGRAPHIC METHODS matography (PC). Column chromatography is subdivided
further into five major column types which constitute
There is an old Dutch word for chemistry, Scheikunde, HPLC. They are (1) liquid–solid chromatography (LSC),
which literally means the art of separation. Indeed, sep- (2) liquid–liquid or partition chromatography (LLC), (3)
aration methods from the chemical substance ultimately bonded-phase chromatography (BPC), (4) ion exchange
depends on separative operations. chromatography(IEC),and(5)exclusionchromatography
Chromatographic methods occupy a rather unique posi- (EC). The latter form includes gel permeation chromatog-
tion among modern methods in the field of detection, sepa- raphy (GPC) and gel filtration chromatography (GFC).
ration, and identification of organic compounds. The latest GLC and HPLC are the most widely used techniques
chromatographic methods provide simple techniques for for separation of organic compounds. However, they are
separation, purification, and structure determination of or- distinctly different techniques. For GC analysis the sam-
ganic compounds including the most complicated natural ple must be volatile and stable when the column is heated.
and synthetic macromolecules in biological and geologi- Samples for liquid chromatography must be soluble in
cal systems and their metabolic or breakdown products. mobile phase and differentially retarded by the station-
Chromatography permits the separation and partial de- ary phase. An active mobile phase increases the versatil-
scription of substances whose presence is unknown or un- ity of the liquid chromatographic technique. By contrast
suspected. As an exploratory method, chromatography is the mobile phase in GC is an inert gas which does not
indispensable in all sciences dealing with chemical sub- influence the separation. A variety of stationary phases
stances and their reactions. Chromatography is, in fact, (both polar and nonpolar) can be used. The versatility of
a physical method of separation in which mixtures are liquid chromatography depends on the liquid phase and
separated by distribution between two phases: a mobile solid absorbent. Gases, liquids, and solids can be ana-
phase and a stationary phase. The mobile phase can be a lyzed by GC. The normal range of molecular weights is
gas (as in gas chromatography) or a liquid (as in liquid from 2 to 500, although derivatives of carbohydrates rang-
chromatography). ing up to 1800 have been analyzed. Liquid chromatog-
Chromatographic methods can be classified according raphy is applicable to liquids and solids that are either
to the nature of the stationary phase. Gas chromatog- ionic or covalently bonded. Molecular weights of 32 to
raphy is divided into GLC and gas–solid chromatogra- 1,000,000 have been analyzed byLC. The flame ionization