Page 41 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioChemistry
P. 41
P1: FPP Final
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN006C-254 June 28, 2001 19:52
Food Colors 113
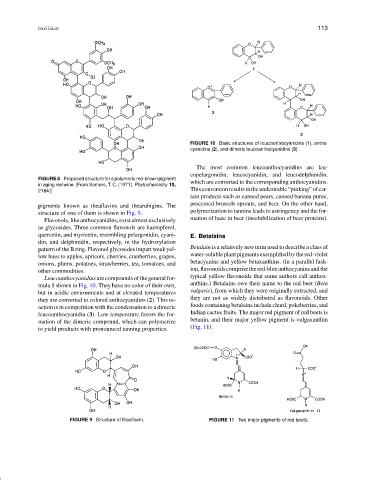
FIGURE 10 Basic structures of leucoanthocyanidins (1), antho-
cyanidins (2), and dimeric leucoanthocyanidins (3).
The most common leucoanthocyanidins are leu-
copelargonidin, leucocyanidin, and leucodelphinidin,
FIGURE 8 Proposed structure for a polymeric red-brown pigment
which are converted to the corresponding anthocyanidins.
in aging red wine. [From Somers, T. C. (1971). Phytochemistry 10,
Thisconversionresultsintheundesirable“pinking”ofcer-
2184.]
tain products such as canned pears, canned banana puree,
processed brussels sprouts, and beer. On the other hand,
pigments known as theaflavins and thearubigins. The
polymerization to tannins leads to astringency and the for-
structure of one of them is shown in Fig. 9.
mation of haze in beer (insolubilization of beer proteins).
Flavonols, like anthocyanidins, exist almost exclusively
as glycosides. Three common flavonols are kaempferol,
quercetin, and myricetin, resembling pelargonidin, cyani- E. Betalains
din, and delphinidin, respectively, in the hydroxylation
pattern of the B ring. Flavonol glycosides impart weak yel- Betalain is a relatively new term used to describe a class of
low hues to apples, apricots, cherries, cranberries, grapes, water-soluble plant pigments exemplified by the red-violet
onions, plums, potatoes, strawberries, tea, tomatoes, and betacyanins and yellow betaxanthins. (In a parallel fash-
other commodities. ion,flavonoidscomprisethered-blueanthocyaninsandthe
Leucoanthocyanidins are compounds of the general for- typical yellow flavonoids that some authors call anthox-
mula 1 shown in Fig. 10. They have no color of their own, anthins.) Betalains owe their name to the red beet (Beta
but in acidic environments and at elevated temperatures vulgaris), from which they were originally extracted, and
they are converted to colored anthocyanidins (2). This re- they are not as widely distributed as flavonoids. Other
foods containing betalains include chard, pokeberries, and
action is in competition with the condensation to a dimeric
Indian cactus fruits. The major red pigment of red beets is
leucoanthocyanidin (3). Low temperature favors the for-
betanin, and their major yellow pigment is vulgaxanthin
mation of the dimeric compound, which can polymerize
(Fig. 11).
to yield products with pronounced tanning properties.
FIGURE 9 Structure of theaflavin. FIGURE 11 Two major pigments of red beets.