Page 183 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd InOrganic Chemistry
P. 183
P1: GTV Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN008H-970 June 29, 2001 16:46
Liquid Alkali Metals 663
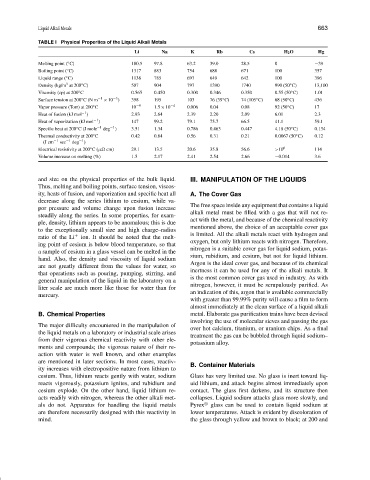
TABLE I Physical Properties of the Liquid Alkali Metals
Li Na K Rb Cs H 2 O Hg
◦
Melting point ( C) 180.5 97.8 63.2 39.0 28.5 0 −39
◦
Boiling point ( C) 1317 883 754 688 671 100 357
Liquid range ( C) 1138 785 697 649 642 100 396
◦
3
◦
◦
Density (kg/m at 200 C) 507 904 797 1390 1740 990 (50 C) 13,100
Viscosity (cp) at 200 C 0.565 0.450 0.300 0.346 0.350 0.55 (50 C) 1.01
◦
◦
◦
◦
◦
◦
Surface tension at 200 C(Nm −1 × 10 −3 ) 398 195 103 76 (39 C) 74 (105 C) 68 (50 C) 436
Vapor pressure (Torr) at 200 C 10 −9 1.5 × 10 −4 0.006 0.04 0.08 92 (50 C) 17
◦
◦
Heat of fusion (kJ mol −1 ) 2.93 2.64 2.39 2.20 2.09 6.01 2.3
Heat of vaporization (kJ mol −1 ) 147 99.2 79.1 75.7 66.5 41.1 59.1
◦
◦
Specific heat at 200 C (J mole −1 deg −1 ) 3.51 1.34 0.786 0.463 0.447 4.18 (50 C) 0.134
◦
Thermal conductivity at 200 C 0.42 0.84 0.56 0.31 0.21 0.0067 (50 C) 0.12
◦
(J cm −1 sec −1 deg −1 )
Electrical resistivity at 200 C(µ cm) 29.1 13.5 20.6 35.8 56.6 >10 6 114
◦
Volume increase on melting (%) 1.5 2.17 2.41 2.54 2.66 −0.014 3.6
and size on the physical properties of the bulk liquid. III. MANIPULATION OF THE LIQUIDS
Thus, melting and boiling points, surface tension, viscos-
ity, heats of fusion, and vaporization and specific heat all A. The Cover Gas
decrease along the series lithium to cesium, while va-
The free space inside any equipment that contains a liquid
por pressure and volume change upon fusion increase
steadily along the series. In some properties, for exam- alkali metal must be filled with a gas that will not re-
act with the metal, and because of the chemical reactivity
ple, density, lithium appears to be anomalous; this is due
mentioned above, the choice of an acceptable cover gas
to the exceptionally small size and high charge–radius
is limited. All the alkali metals react with hydrogen and
ratio of the Li + ion. It should be noted that the melt-
oxygen, but only lithium reacts with nitrogen. Therefore,
ing point of cesium is below blood temperature, so that
nitrogen is a suitable cover gas for liquid sodium, potas-
a sample of cesium in a glass vessel can be melted in the
sium, rubidium, and cesium, but not for liquid lithium.
hand. Also, the density and viscosity of liquid sodium
Argon is the ideal cover gas, and because of its chemical
are not greatly different from the values for water, so
inertness it can be used for any of the alkali metals. It
that operations such as pouring, pumping, stirring, and
is the most common cover gas used in industry. As with
general manipulation of the liquid in the laboratory on a
nitrogen, however, it must be scrupulously purified. As
liter scale are much more like those for water than for
an indication of this, argon that is available commercially
mercury.
with greater than 99.99% purity will cause a film to form
almost immediately at the clean surface of a liquid alkali
B. Chemical Properties metal. Elaborate gas purification trains have been devised
involving the use of molecular sieves and passing the gas
The major difficulty encountered in the manipulation of
over hot calcium, titanium, or uranium chips. As a final
the liquid metals on a laboratory or industrial scale arises
treatment the gas can be bubbled through liquid sodium–
from their vigorous chemical reactivity with other ele-
potassium alloy.
ments and compounds; the vigorous nature of their re-
action with water is well known, and other examples
are mentioned in later sections. In most cases, reactiv- B. Container Materials
ity increases with electropositive nature from lithium to
cesium. Thus, lithium reacts gently with water, sodium Glass has very limited use. No glass is inert toward liq-
reacts vigorously, potassium ignites, and rubidium and uid lithium, and attack begins almost immediately upon
cesium explode. On the other hand, liquid lithium re- contact. The glass first darkens, and its structure then
acts readily with nitrogen, whereas the other alkali met- collapses. Liquid sodium attacks glass more slowly, and
als do not. Apparatus for handling the liquid metals Pyrex glass can be used to contain liquid sodium at
are therefore necessarily designed with this reactivity in lower temperatures. Attack is evident by discoloration of
mind. the glass through yellow and brown to black; at 200 and