Page 213 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd InOrganic Chemistry
P. 213
P1: GSS Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN009F-398 July 6, 2001 20:34
22 Main Group Elements
Concentrated H 3 PO 4 is one of the most important acids the enzymes known as kinases, phosphorylases, and phos-
of the chemical industry; more than 10 billion kg are pro- photransferases, all of which involve phosphate esters or
duced annually. The reactions for the preparation and use anhydrides.
of phosphoric acid can be summarized as follows:
Ca 5 (PO 4 ) 3 F + 10H 2 O + 5H 2 SO 4 G. Aluminophosphates
Phosphate
rock
→ 3H 3 PO 4 + 5CaSO 4 · 2H 2 O + HF A new family of aluminophosphate molecular sieves has
Impure been developed. The aluminophosphates are microporous
acid
inorganic solids with structural and chemical properties
P 4 + 5O 2 → P 4 O 10 similar to those of zeolites, which are naturally occur-
Elemental
phosphorus ring and synthetic aluminosilicates. Natural zeolites find
(prepared from applications as molecular sieves, ion exchangers, water
phosphate rock)
softeners, and desiccating agents. The new aluminophos-
then
phate sieves (AlPO 4 ) are strongly hydrophilic and pref-
P 4 O 10 + 6H 2 O → 4H 3 PO 4
Pure phosphoric erentially adsorb water over hydrocarbons. Their poten-
acid tial use as desiccants in drying large volumes of natural
About 95% of the impure phosphoric acid is used to
gases has been suggested. Unlike the zeolites, however,
prepare fertilizers; the remainder is made into pure phos-
the aluminophosphates apparently lack ion-exchange ca-
phoric acid for metal treatment or use in foods, detergents,
pability. Of greater importance to the chemical industry is
and pharmaceuticals.
the possible application of the aluminophosphates as cat-
alysts and catalyst supports in reforming and isomerizing
F. Metaphosphate Ions
hydrocarbons.
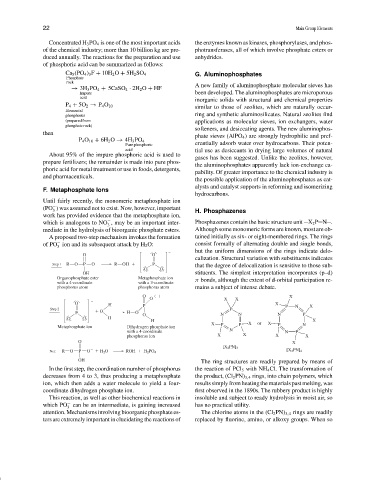
Until fairly recently, the monomeric metaphosphate ion
−
(PO ) was assumed not to exist. Now, however, important H. Phosphazenes
3
work has provided evidence that the metaphosphate ion,
−
which is analogous to NO , may be an important inter- Phosphazenes contain the basic structure unit X 2 P N .
3
mediate in the hydrolysis of bioorganic phosphate esters. Although some monomeric forms are known, most are ob-
A proposed two-step mechanism invokes the formation tained initially as six- or eight-membered rings. The rings
of PO ion and its subsequent attack by H 2 O: consist formally of alternating double and single bonds,
−
3
but the uniform dimensions of the rings indicate delo-
O O
calization. Structural variation with substituents indicates
Step 1 R O P O R OH P that the degree of delocalization is sensitive to those sub-
O O
OH stituents. The simplest interpretation incorporates (p–d)
Organophosphate ester Metaphosphate ion π bonds, although the extent of d-orbital participation re-
with a 4-coordinate with a 3-coordinate
phosphorus atom phosphorus atom mains a subject of intense debate.
O ( ) X
O X X
O H P X X
Step 2 O P P N
P H O O N N N P
O O H
H X
X P P X or X P N
Metaphosphate ion Dihydrogen phosphate ion
with a 4-coordinate N N P
phosphorus ion X X X X
O X
[X 2 PN] 3
Net: R O P O H 2 O ROH H 2 PO 4 [X 2 PN] 4
OH The ring structures are readily prepared by means of
In the first step, the coordination number of phosphorus the reaction of PCl 5 with NH 4 Cl. The transformation of
decreases from 4 to 3, thus producing a metaphosphate the product, (Cl 2 PN) 3,4 rings, into chain polymers, which
ion, which then adds a water molecule to yield a four- results simply from heating the materials past melting, was
coordinate dihydrogen phosphate ion. first observed in the 1890s. The rubbery product is highly
This reaction, as well as other biochemical reactions in insoluble and subject to ready hydrolysis in moist air, so
which PO can be an intermediate, is gaining increased has no practical utility.
−
3
attention.Mechanismsinvolvingbioorganicphosphatees- The chlorine atoms in the (Cl 2 PN) 3,4 rings are readily
ters are extremely important in elucidating the reactions of replaced by fluorine, amino, or alkoxy groups. When so