Page 215 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd InOrganic Chemistry
P. 215
P1: GSS Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN009F-398 July 6, 2001 20:34
24 Main Group Elements
with a slight reddish tint, bismuth is one of the few sub- phosphorus, oxygen is one of the major elements of the
stances that expands on freezing. Most bismuth is used to bioorganic compounds of living organisms—the lipids,
prepare low-melting alloys composed of bismuth, tin, and carbohydrates, proteins, and vitamins.
lead. Rose’s metal, which contains 50% bismuth, 25% Among the top 50 chemicals produced in 1989, oxygen
◦
lead, and 25% tin, melts at 94 C; and Wood’s metal, in ranked third, with 17.2 billion kg; however, in terms of
which half the tin is replaced with cadmium, melts at only moles it would have earned fourth place, with 536 billion
◦
65.5 C. These remarkably low-melting alloys are used in mol.
automatic sprinkler systems and fire alarms. Nearly all oxygen is prepared by fractional distillation
A minor use of bismuth, which has not been demon- of air, and most of the huge amount produced is used for
strated as being poisonous, is its application in pharma- steelmaking and welding purposes. Oxygen finds consid-
ceutical compounds. erable application in medicine, and a significant quantity
of liquid oxygen is employed as the oxidant in rocket fuels.
A. Hydrides
The three hydrides of arsenic, antimony, and bismuth are A. Allotropes
arsine (AsH 3 ), stibine (SbH 3 ), and bismuthine (BiH 3 ); all
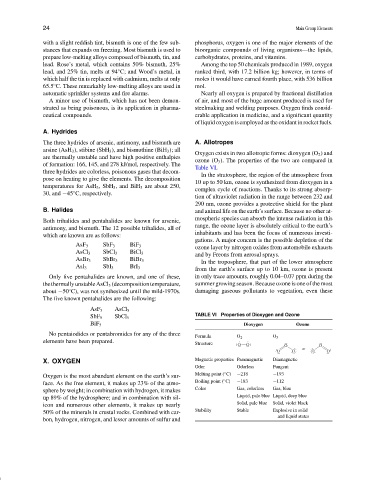
Oxygen exists in two allotropic forms: dioxygen (O 2 ) and
are thermally unstable and have high positive enthalpies
ozone (O 3 ). The properties of the two are compared in
of formation: 166, 145, and 278 kJ/mol, respectively. The
Table VI.
three hydrides are colorless, poisonous gases that decom-
In the stratosphere, the region of the atmosphere from
pose on heating to give the elements. The decomposition
10 up to 50 km, ozone is synthesized from dioxygen in a
temperatures for AsH 3 , SbH 3 , and BiH 3 are about 250,
complex cycle of reactions. Thanks to its strong absorp-
◦
30, and −45 C, respectively.
tion of ultraviolet radiation in the range between 232 and
290 nm, ozone provides a protective shield for the plant
B. Halides and animal life on the earth’s surface. Because no other at-
mospheric species can absorb the intense radiation in this
Both trihalides and pentahalides are known for arsenic,
range, the ozone layer is absolutely critical to the earth’s
antimony, and bismuth. The 12 possible trihalides, all of
which are known are as follows: inhabitants and has been the focus of numerous investi-
gations. A major concern is the possible depletion of the
AsF 3 SbF 3 BiF 3
ozone layer by nitrogen oxides from automobile exhausts
AsCl 3 SbCl 3 BiCl 3
and by Freons from aerosal sprays.
AsBr 3 SbBr 3 BiBr 3
In the troposphere, that part of the lower atmosphere
AsI 3 SbI 3 BrI 3
from the earth’s surface up to 10 km, ozone is present
Only five pentahalides are known, and one of these, in only trace amounts, roughly 0.04–0.07 ppm during the
thethermallyunstableAsCl 5 (decompositiontemperature, summer growing season. Because ozone is one of the most
◦
about −50 C), was not synthesized until the mild-1970s. damaging gaseous pollutants to vegetation, even these
The five known pentahalides are the following:
AsF 5 AsCl 5
TABLE VI Properties of Dioxygen and Ozone
SbF 5 SbCl 5
BiF 5 Dioxygen Ozone
No pentaiodides or pentabromides for any of the three
Formula O 2 O 3
elements have been prepared.
Structure O O O O
or
O O O O
X. OXYGEN Magnetic properties Paramagnetic Diamagnetic
Odor Odorless Pungent
◦
Oxygen is the most abundant element on the earth’s sur- Melting point ( C) −218 −193
◦
face. As the free element, it makes up 23% of the atmo- Boiling point ( C) −183 −112
sphere by weight; in combination with hydrogen, it makes Color Gas, colorless Gas, blue
up 89% of the hydrosphere; and in combination with sil- Liquid, pale blue Liquid, deep blue
icon and numerous other elements, it makes up nearly Solid, pale blue Solid, violet black
50% of the minerals in crustal rocks. Combined with car- Stability Stable Explosive in solid
and liquid states
bon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and lesser amounts of sulfur and