Page 397 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd InOrganic Chemistry
P. 397
P1: GQT/GRI P2: GTV/FFV P3: GTV/FFV QC: GSS Final pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN014A-653 July 28, 2001 20:55
Rare Earth Elements and Materials 21
the boiling point of liquid nitrogen, and significant com- the high Tc substances. The inherent brittleness of ceram-
mercial opportunities were forecast. The race to discover ics prevents their fabrication into wires, and it now seems
the chemical composition and crystal structure of the sin- that the most promising way forward is the deposition of
gle phase responsible for the superconductivity was one of thin films of superconductor onto metal oxide or silver
the most competitive and intense in the history of science. surfaces to form flexible tapes.
BylateMarch1987,becauseofreportsfromNRCCanada,
Bellcore, AT&T Bell Laboratories, Argonne National
Laboratories, McMaster University, and others, the com- V. CATALYSIS AND OTHER
pound was identified as YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7 . CHEMICAL APPLICATIONS
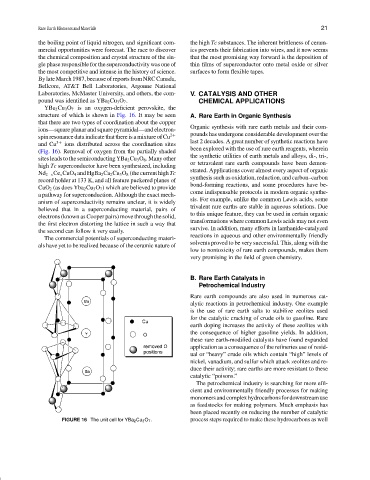
YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7 is an oxygen-deficient perovskite, the
structure of which is shown in Fig. 16. It may be seen A. Rare Earth in Organic Synthesis
that there are two types of coordination about the copper
Organic synthesis with rare earth metals and their com-
ions—square planar and square pyramidal—and electron-
pounds has undergone considerable development over the
spin resonance data indicate that there is a mixture of Cu 2+
3+ last 2 decades. A great number of synthetic reactions have
and Cu ions distributed across the coordination sites
been explored with the use of rare earth reagents, wherein
(Fig. 16). Removal of oxygen from the partially shaded
the synthetic utilities of earth metals and alloys, di-, tri-,
sites leads to the semiconducting YBa 2 Cu 3 O 6 . Many other
or tetravalent rare earth compounds have been demon-
high Tc superconductor have been synthesized, including
strated. Applications cover almost every aspect of organic
Nd 2−x Ce x CuO 4 and HgBa 2 Ca 2 Cu 3 O 8 (the current high Tc
synthesis such as oxidation, reduction, and carbon–carbon
record holder at 133 K, and all feature puckered planes of
bond-forming reactions, and some procedures have be-
CuO 2 (as does Yba 2 Cu 3 O 7 ) which are believed to provide
come indispensable protocols in modern organic synthe-
a pathway for superconduction. Although the exact mech-
sis. For example, unlike the common Lewis acids, some
anism of superconductivity remains unclear, it is widely
trivalent rare earths are stable in aqueous solutions. Due
believed that in a superconducting material, pairs of
to this unique feature, they can be used in certain organic
electrons (known as Cooper pairs) move through the solid,
transformations where common Lewis acids may not even
the first electron distorting the lattice in such a way that
survive. In addition, many efforts in lanthanide-catalyzed
the second can follow it very easily.
reactions in aqueous and other environmentally friendly
The commercial potentials of superconducting materi-
solvents proved to be very successful. This, along with the
als have yet to be realized because of the ceramic nature of
low to nontoxicity of rare earth compounds, makes them
very promising in the field of green chemistry.
B. Rare Earth Catalysts in
Petrochemical Industry
Rare earth compounds are also used in numerous cat-
alytic reactions in petrochemical industry. One example
is the use of rare earth salts to stabilize zeolites used
for the catalytic cracking of crude oils to gasoline. Rare
earth doping increases the activity of these zeolites with
the consequence of higher gasoline yields. In addition,
these rare earth-modified catalysts have found expanded
application as a consequence of the refineries use of resid-
ual or “heavy” crude oils which contain “high” levels of
nickel, vanadium, and sulfur which attack zeolites and re-
duce their activity; rare earths are more resistant to these
catalytic “poisons.”
The petrochemical industry is searching for more effi-
cient and environmentally friendly processes for making
monomers and complex hydrocarbons for downstream use
as feedstocks for making polymers. Much emphasis has
been placed recently on reducing the number of catalytic
FIGURE 16 The unit cell for YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7 . process steps required to make these hydrocarbons as well