Page 49 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd InOrganic Chemistry
P. 49
P1: ZBU Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002F-55 May 22, 2001 21:6
Bioinorganic Chemistry 137
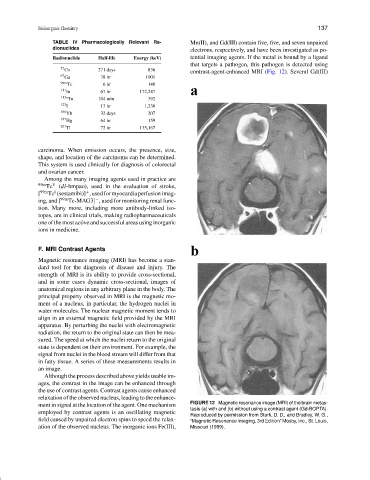
TABLE IV Pharmacologically Relevant Ra- Mn(II), and Gd(III) contain five, five, and seven unpaired
dionuclides electrons, respectively, and have been investigated as po-
Radionuclide Half-life Energy (keV) tential imaging agents. If the metal is bound by a ligand
that targets a pathogen, this pathogen is detected using
57 Co 271 days 836 contrast-agent-enhanced MRI (Fig. 12). Several Gd(III)
67 Ga 78 hr 1001
99m Tc 6 hr 140
111 In 67 hr 172,247
113m In 104 min 392
123 I 13 hr 1,230
169 Yb 32 days 207
197 Hg 64 hr 159
201
Tl 72 hr 135,167
carcinoma. When emission occurs, the presence, size,
shape, and location of the carcinoma can be determined.
This system is used clinically for diagnosis of colorectal
and ovarian cancer.
Among the many imaging agents used in practice are
99m Tc V (dl-hmpao), used in the evaluation of stroke,
I
[ 99m Tc (sestamibi)] ,usedformyocardiaperfusionimag-
+
ing, and [ 99m Tc-MAG3] , used for monitoring renal func-
−
tion. Many more, including more antibody-linked iso-
topes, are in clinical trials, making radiopharmaceuticals
one of the most active and successful areas using inorganic
ions in medicine.
F. MRI Contrast Agents
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has become a stan-
dard tool for the diagnosis of disease and injury. The
strength of MRI is its ability to provide cross-sectional,
and in some cases dynamic cross-sectional, images of
anatomical regions in any arbitrary plane in the body. The
principal property observed in MRI is the magnetic mo-
ment of a nucleus, in particular, the hydrogen nuclei in
water molecules. The nuclear magnetic moment tends to
align in an external magnetic field provided by the MRI
apparatus. By perturbing the nuclei with electromagnetic
radiation, the return to the original state can then be mea-
sured. The speed at which the nuclei return to the original
state is dependent on their environment. For example, the
signal from nuclei in the blood stream will differ from that
in fatty tissue. A series of these measurements results in
an image.
Although the process described above yields usable im-
ages, the contrast in the image can be enhanced through
the use of contrast agents. Contrast agents cause enhanced
relaxation of the observed nucleus, leading to the enhance-
ment in signal at the location of the agent. One mechanism FIGURE 12 Magnetic resonance image (MRI) of the brain metas-
tasis (a) with and (b) without using a contrast agent (Gd-BOPTA).
employed by contrast agents is an oscillating magnetic
Reproduced by permission from Stark, D. D., and Bradley, W. G.,
field caused by unpaired electron spins to speed the relax- “Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 3rd Edition” Mosby, Inc., St. Louis,
ation of the observed nucleus. The inorganic ions Fe(III), Missouri (1999).