Page 65 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd InOrganic Chemistry
P. 65
P1: LLL Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002c-73 May 21, 2001 13:59
314 Boron Hydrides
With difunctional reagents and the dilithium salts, ortho-
carborane behaves quite differently than the other two iso-
mers. The proximity of the two carbon atoms on ortho-
carborane leads to the formation of rings, but for the meta
and para isomers the carbon atoms are remote enough
from each other that rings are precluded and polymers
can be formed. The meta isomer has generally been em-
ployed in these reactions since it is easily prepared es-
sentially pure from the ortho isomer, whereas prepara-
tion of the para isomer requires separating it from the
meta form. Short inorganic and organic links between the
carborane residues have been used to prepare carborane
resins. Longer and more flexible methyl-siloxane links
between meta carborane residues have resulted in flexible
elastomers with excellent resistance to high temperatures.
This resistance may be the result of the bulky carborane
cages blocking the formation of siloxane rings, a principle
mode of siloxane polymer decomposition.
Electrophylic substitutions have been studied exten-
sively for the icosahedral carboranes. Because of the
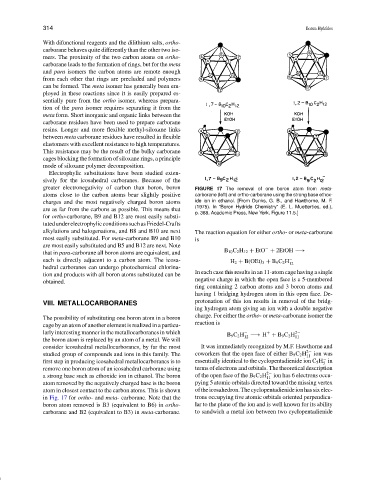
greater electronegativity of carbon than boron, boron FIGURE 17 The removal of one boron atom from meta-
atoms close to the carbon atoms bear slightly positive carborane (left) and ortho-carborane using the strong base ethox-
charges and the most negatively charged boron atoms ide ion in ethanol. [From Dunks, G. B., and Hawthorne, M. F.
are as far from the carbons as possible. This means that (1975). In “Boron Hydride Chemistry” (E. L. Muetterties, ed.),
p. 388, Academic Press, New York, Figure 11.5.]
for ortho-carborane, B9 and B12 are most easily substi-
tutedunderelectrophylicconditionssuchasFriedel-Crafts
alkylations and halogenations, and B8 and B10 are next The reaction equation for either ortho-or meta-carborane
most easily substituted. For meta-carborane B9 and B10 is
are most easily substituted and B5 and B12 are next. Note
−
that in para-carborane all boron atoms are equivalent, and B 10 C 2 H 12 + EtO + 2EtOH −→
each is directly adjacent to a carbon atom. The icosa- H 2 + B(OEt) 3 + B 9 C 2 H −
12
hedral carboranes can undergo photochemical chlorina-
In each case this results in an 11-atom cage having a single
tion and products with all boron atoms substituted can be
negative charge in which the open face is a 5-membered
obtained.
ring containing 2 carbon atoms and 3 boron atoms and
having 1 bridging hydrogen atom in this open face. De-
VIII. METALLOCARBORANES protonation of this ion results in removal of the bridg-
ing hydrogen atom giving an ion with a double negative
charge. For either the ortho-or meta-carborane isomer the
The possibility of substituting one boron atom in a boron
reaction is
cage by an atom of another element is realized in a particu-
larly interesting manner in the metallocarboranes in which B 9 C 2 H − −→ H + B 9 C 2 H 2−
+
11
12
the boron atom is replaced by an atom of a metal. We will
consider icosahedral metallocarboranes, by far the most It was immediately recognized by M.F. Hawthorne and
studied group of compounds and ions in this family. The coworkers that the open face of either B 9 C 2 H 2− ion was
11
−
first step in producing icosahedral metallocarboranes is to essentially identical to the cyclopentadienide ion C 5 H in
5
remove one boron atom of an icosahedral carborane using terms of electrons and orbitals. The theoretical description
a strong base such as ethoxide ion in ethanol. The boron of the open face of the B 9 C 2 H 2− ion has 6 electrons occu-
11
atom removed by the negatively charged base is the boron pying 5 atomic orbitals directed toward the missing vertex
atom in closest contact to the carbon atoms. This is shown oftheicosahedron.Thecyclopentadienideionhassixelec-
in Fig. 17 for ortho- and meta- carborane. Note that the trons occupying five atomic orbitals oriented perpendicu-
boron atom removed is B3 (equivalent to B6) in ortho- lar to the plane of the ion and is well known for its ability
carborane and B2 (equivalent to B3) in meta-carborane. to sandwich a metal ion between two cyclopentadienide