Page 27 - Subyek Encyclopedia - Encyclopedia of Separation Science
P. 27
22 I / CENTRIFUGATION/ Derivatization
or the pressure generated by the centrifugal force is If the resistance of the Rlter is negligible, P is
substituted for the gravitational or differential- equivalent to the centrifugal pressure. A parameter
pressure terms. As Rltration is an extensively charac- that is widely used to characterize the performance of
terized Reld of study, a description of which is beyond Rltration equipment is the drainage number:
the scope of this article, it is recommended that the
1/2
reader refer to the literature for an in-depth math- Drainage number"d M (G) / [26]
ematical discussion of both conventional and centri-
fugal Rltration. However, a brief summary of some of where d M is the mean particle diameter ( m); G is the
2
the more important parameters that govern Sow velo- centrifugal force (" r/g), where r is the largest
city and pressure drop during centrifugal Rltration radius for a variable radius screen; and is the Rltrate
1
2
follow. A simple basket centrifuge is shown schemati- viscosity (m s ). Higher drainage numbers corres-
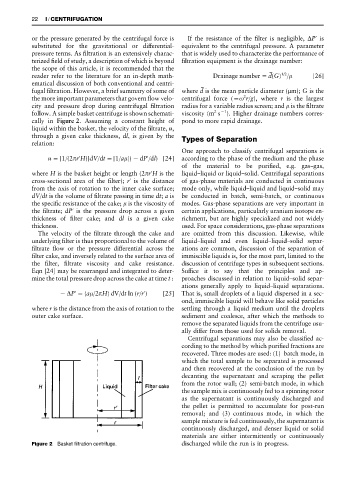
cally in Figure 2. Assuming a constant height of pond to more rapid drainage.
liquid within the basket, the velocity of the Rltrate, u,
through a given cake thickness, dl, is given by the Types of Separation
relation:
One approach to classify centrifugal separations is
u"[1/(2 r H)]dV/dt"[1/a ](!dP /dl) [24] according to the phase of the medium and the phase
of the material to be puriRed, e.g. gas}gas,
where H is the basket height or length (2 r H is the liquid}liquid or liquid}solid. Centrifugal separations
cross-sectional area of the Rlter); r is the distance of gas-phase materials are conducted in continuous
from the axis of rotation to the inner cake surface; mode only, while liquid}liquid and liquid}solid may
dV/dt is the volume of Rltrate passing in time dt; a is be conducted in batch, semi-batch, or continuous
the speciRc resistance of the cake; is the viscosity of modes. Gas-phase separations are very important in
the Rltrate; dP is the pressure drop across a given certain applications, particularly uranium isotope en-
thickness of Rlter cake; and dl is a given cake richment, but are highly specialized and not widely
thickness. used. For space considerations, gas-phase separations
The velocity of the Rltrate through the cake and are omitted from this discussion. Likewise, while
underlying Rlter is thus proportional to the volume of liquid}liquid and even liquid}liquid}solid separ-
Rltrate Sow or the pressure differential across the ations are common, discussion of the separation of
Rlter cake, and inversely related to the surface area of immiscible liquids is, for the most part, limited to the
the Rlter, Rltrate viscosity and cake resistance. discussion of centrifuge types in subsequent sections.
Eqn [24] may be rearranged and integrated to deter- SufRce it to say that the principles and ap-
mine the total pressure drop across the cake at time t : proaches discussed in relation to liquid}solid separ-
ations generally apply to liquid}liquid separations.
! P "(a /2 H)dV/dt ln (r/r ) [25] That is, small droplets of a liquid dispersed in a sec-
ond, immiscible liquid will behave like solid particles
where r is the distance from the axis of rotation to the settling through a liquid medium until the droplets
outer cake surface. sediment and coalesce, after which the methods to
remove the separated liquids from the centrifuge usu-
ally differ from those used for solids removal.
Centrifugal separations may also be classiRed ac-
cording to the method by which puriRed fractions are
recovered. Three modes are used: (1) batch mode, in
which the total sample to be separated is processed
and then recovered at the conclusion of the run by
decanting the supernatant and scraping the pellet
from the rotor wall; (2) semi-batch mode, in which
the sample mix is continuously fed to a spinning rotor
as the supernatant is continuously discharged and
the pellet is permitted to accumulate for post-run
removal; and (3) continuous mode, in which the
sample mixture is fed continuously, the supernatant is
continuously discharged, and denser liquid or solid
materials are either intermittently or continuously
Figure 2 Basket filtration centrifuge. discharged while the run is in progress.