Page 207 - Energy from Toxic Organic Waste for Heat and Power Generation
P. 207
Power Generation From Renewable Energy Sources 185
taking place inside the engine cylinder caused by fuel properties of liq-
uid fuel blends and better mixing of air and fuel combinations results in
higher NO x emissions. Formation of homogeneous mixture and enhanced
ignition centers caused by squish and swirl generated are also responsible
for the observed trends. Further marginal increase in delay period, higher
energy content of fuel blends, and presence of oxygen in HOME were
better utilized when dual fuel operation happens with RCC. Therefore, it
has resulted in slightly higher peak cycle temperature. The NO x levels for
HOME-PG(HCC) and HOME-PG(RCC) operation with 10%, 20%, and
30% fuel oil were found to be 80, 91, 96 ppm and 109 ppm, respectively,
compared to 120 ppm for diesel-PG operation (HCC).
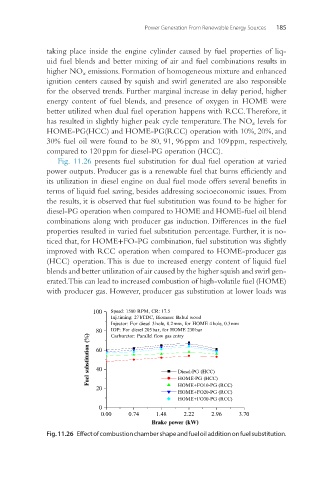
Fig. 11.26 presents fuel substitution for dual fuel operation at varied
power outputs. Producer gas is a renewable fuel that burns efficiently and
its utilization in diesel engine on dual fuel mode offers several benefits in
terms of liquid fuel saving, besides addressing socioeconomic issues. From
the results, it is observed that fuel substitution was found to be higher for
diesel-PG operation when compared to HOME and HOME-fuel oil blend
combinations along with producer gas induction. Differences in the fuel
properties resulted in varied fuel substitution percentage. Further, it is no-
ticed that, for HOME+FO-PG combination, fuel substitution was slightly
improved with RCC operation when compared to HOME-producer gas
(HCC) operation. This is due to increased energy content of liquid fuel
blends and better utilization of air caused by the higher squish and swirl gen-
erated. This can lead to increased combustion of high-volatile fuel (HOME)
with producer gas. However, producer gas substitution at lower loads was
100 Speed: 1500 RPM, CR: 17.5
Inj.timing: 27bTDC, Biomass: Babul wood
Injector: For diesel 3hole, 0.2 mm, for HOME 4hole, 0.3mm
80 IOP: For diesel 205bar, for HOME 230bar
Carburetor: Parallel flow gas entry
Fuel substitution (%) 60 Diesel-PG (HCC)
40
HOME+FO10-PG (RCC)
20 HOME-PG (HCC)
HOME+FO20-PG (RCC)
HOME+FO30-PG (RCC)
0
0.00 0.74 1.48 2.22 2.96 3.70
Brake power (kW)
Fig. 11.26 Effect of combustion chamber shape and fuel oil addition on fuel substitution.