Page 23 - Energy from Toxic Organic Waste for Heat and Power Generation
P. 23
12 Energy from Toxic Organic Waste for Heat and Power Generation
Syngas
treatment
Raw Clean
Exhaust gases
syngas syngas
Biomass
Pyrolyzer
Post Char
combustor
Tar Syngas
Heat compressor
exchanger Reg
Rec
Flue gases
treatment
Air Gas turbine
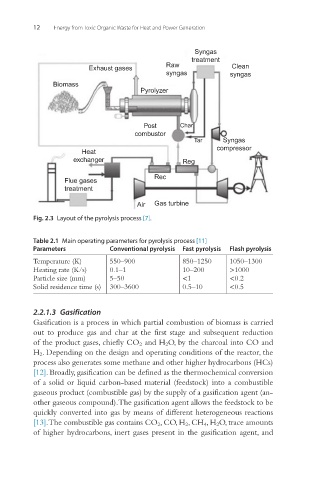
Fig. 2.3 Layout of the pyrolysis process [7].
Table 2.1 Main operating parameters for pyrolysis process [11]
Parameters Conventional pyrolysis Fast pyrolysis Flash pyrolysis
Temperature (K) 550–900 850–1250 1050–1300
Heating rate (K/s) 0.1–1 10–200 >1000
Particle size (mm) 5–50 <1 <0.2
Solid residence time (s) 300–3600 0.5–10 <0.5
2.2.1.3 Gasification
Gasification is a process in which partial combustion of biomass is carried
out to produce gas and char at the first stage and subsequent reduction
of the product gases, chiefly CO 2 and H 2 O, by the charcoal into CO and
H 2 . Depending on the design and operating conditions of the reactor, the
process also generates some methane and other higher hydrocarbons (HCs)
[12]. Broadly, gasification can be defined as the thermochemical conversion
of a solid or liquid carbon-based material (feedstock) into a combustible
gaseous product (combustible gas) by the supply of a gasification agent (an-
other gaseous compound). The gasification agent allows the feedstock to be
quickly converted into gas by means of different heterogeneous reactions
[13]. The combustible gas contains CO 2 , CO, H 2 , CH 4 , H 2 O, trace amounts
of higher hydrocarbons, inert gases present in the gasification agent, and