Page 27 - Energy from Toxic Organic Waste for Heat and Power Generation
P. 27
Toxic Waste From Municipality 15
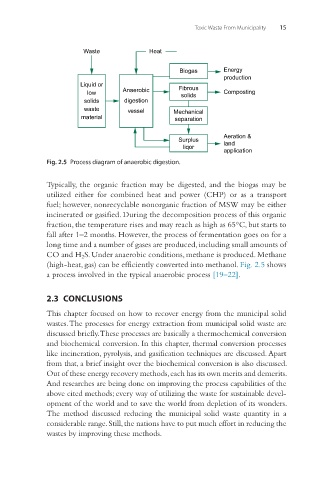
Waste Heat
Biogas Energy
production
Liquid or Fibrous
low Anaerobic solids Composting
solids digestion
waste vessel Mechanical
material separation
Aeration &
Surplus land
liqor
application
Fig. 2.5 Process diagram of anaerobic digestion.
Typically, the organic fraction may be digested, and the biogas may be
utilized either for combined heat and power (CHP) or as a transport
fuel; however, nonrecyclable nonorganic fraction of MSW may be either
incinerated or gasified. During the decomposition process of this organic
fraction, the temperature rises and may reach as high as 65°C, but starts to
fall after 1–2 months. However, the process of fermentation goes on for a
long time and a number of gases are produced, including small amounts of
CO and H 2 S. Under anaerobic conditions, methane is produced. Methane
(high-heat, gas) can be efficiently converted into methanol. Fig. 2.5 shows
a process involved in the typical anaerobic process [19–22].
2.3 CONCLUSIONS
This chapter focused on how to recover energy from the municipal solid
wastes. The processes for energy extraction from municipal solid waste are
discussed briefly. These processes are basically a thermochemical conversion
and biochemical conversion. In this chapter, thermal conversion processes
like incineration, pyrolysis, and gasification techniques are discussed. Apart
from that, a brief insight over the biochemical conversion is also discussed.
Out of these energy recovery methods, each has its own merits and demerits.
And researches are being done on improving the process capabilities of the
above cited methods; every way of utilizing the waste for sustainable devel-
opment of the world and to save the world from depletion of its wonders.
The method discussed reducing the municipal solid waste quantity in a
considerable range. Still, the nations have to put much effort in reducing the
wastes by improving these methods.