Page 68 - Engineering Digital Design
P. 68
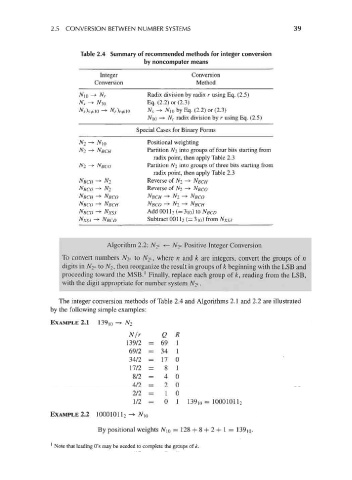
2.5 CONVERSION BETWEEN NUMBER SYSTEMS 39
Table 2.4 Summary of recommended methods for integer conversion
by noncomputer means
Integer Conversion
Conversion Method
Radix division by radix r using Eq. (2.5)
N 10 -> N r
N s -^ NIO Eq. (2.2) or (2.3)
N s).v^]0 -+ NrWic , N, -+ JVio by Eq. (2.2) or (2.3)
NIO —* N r radix division by r using Eq. (2.5)
Special Cases for Binary Forms
N 2 -» NIO Positional weighting
N 2 -> NBCH Partition N 2 into groups of four bits starting from
radix point, then apply Table 2.3
N 2 — > NBCO Partition A^ into groups of three bits starting from
radix point, then apply Table 2.3
Reverse of N2 — > NBCH
NBCH -> N 2
Reverse of N 2 —> NBCO
NBCO -* N 2
NBCH -> NBCO NBCH -> N 2 -+ NBCO
NBCO -» NBCH NBCO -+ N 2 -+ NBCH
N fio) -> %55 Add0011 2 (=3i 0 )toN BC D
NXS^ -> NBCD Subtract 001 1 2 (= 3 10) from NXSB
Algorithm 2.2: #2* •«- N%> Positive Integer Conversion
To convert numbers A/2« to N 2k, where n and k are integers, convert the groups of n
digits in A^2« to A^, then reorganize the result in groups of k beginning with the LSB and
1
proceeding toward the MSB. Finally, replace each group of k, reading from the LSB,
with the digit appropriate for number system #2* •
The integer conversion methods of Table 2.4 and Algorithms 2.1 and 2.2 are illustrated
by the following simple examples:
EXAMPLE 2.1 139, 0 -+ N 2
N/r Q R
139/2 = 69 1
69/2 = 34 1
34/2 = 17 0
17/2 = 8 1
8/ 2 = 4 0
4/ 2 = 2 0
2/ 2 = 1 0
1/2 = 0 1 139i 0= 10001011 2
EXAMPLE 2.2 10001011 2 -> N\ 0
By positional weights N [0 = 128 + 8 + 2 + 1 = 139i 0.
Note that leading O's may be needed to complete the groups of k.