Page 63 - Engineering Digital Design
P. 63
34 CHAPTER 2 / NUMBER SYSTEMS, BINARY ARITHMETIC, AND CODES
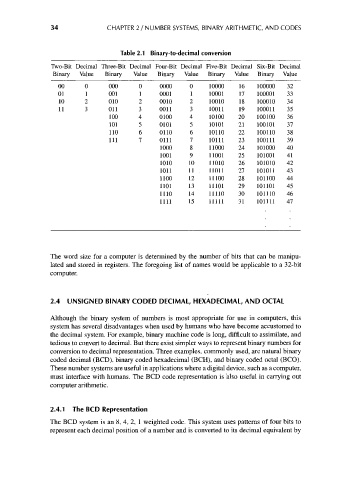
Table 2.1 Binary-to-decimal conversion
Two-Bit Decimal Three-Bit Decimal Four-Bit Decimal Five-Bit Decimal Six-Bit Decimal
Binary Value Binary Value Binary Value Binary Value Binary Value
00 0 000 0 0000 0 10000 16 100000 32
01 1 001 1 0001 1 10001 17 100001 33
10 2 010 2 0010 2 10010 18 100010 34
11 3 Oil 3 0011 3 10011 19 100011 35
100 4 0100 4 10100 20 100100 36
101 5 0101 5 10101 21 100101 37
110 6 0110 6 10110 22 100110 38
111 7 0111 7 10111 23 100111 39
1000 8 11000 24 101000 40
1001 9 11001 25 101001 41
1010 10 11010 26 101010 42
1011 11 11011 27 101011 43
1100 12 11100 28 101100 44
1101 13 11101 29 101101 45
1110 14 11110 30 101110 46
1111 15 11111 31 101111 47
The word size for a computer is determined by the number of bits that can be manipu-
lated and stored in registers. The foregoing list of names would be applicable to a 32-bit
computer.
2.4 UNSIGNED BINARY CODED DECIMAL, HEXADECIMAL, AND OCTAL
Although the binary system of numbers is most appropriate for use in computers, this
system has several disadvantages when used by humans who have become accustomed to
the decimal system. For example, binary machine code is long, difficult to assimilate, and
tedious to convert to decimal. But there exist simpler ways to represent binary numbers for
conversion to decimal representation. Three examples, commonly used, are natural binary
coded decimal (BCD), binary coded hexadecimal (BCH), and binary coded octal (BCO).
These number systems are useful in applications where a digital device, such as a computer,
must interface with humans. The BCD code representation is also useful in carrying out
computer arithmetic.
2.4.1 The BCD Representation
The BCD system is an 8, 4, 2, 1 weighted code. This system uses patterns of four bits to
represent each decimal position of a number and is converted to its decimal equivalent by