Page 222 - Engineering Electromagnetics, 8th Edition
P. 222
204 ENGINEERING ELECTROMAGNETICS
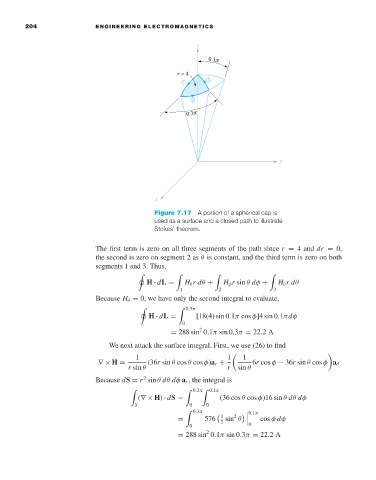
Figure 7.17 A portion of a spherical cap is
used as a surface and a closed path to illustrate
Stokes’ theorem.
The first term is zero on all three segments of the path since r = 4 and dr = 0,
the second is zero on segment 2 as θ is constant, and the third term is zero on both
segments 1 and 3. Thus,
H · dL = H θ rdθ + H φ r sin θ dφ + H θ rdθ
1 2 3
Because H θ = 0, we have only the second integral to evaluate,
0.3π
H · dL = [18(4) sin 0.1π cos φ]4 sin 0.1πdφ
0
2
= 288 sin 0.1π sin 0.3π = 22.2A
We next attack the surface integral. First, we use (26) to find
1 1 1
∇× H = (36r sin θ cos θ cos φ)a r + 6r cos φ − 36r sin θ cos φ a θ
r sin θ r sin θ
2
Because dS = r sin θ dθ dφ a r , the integral is
0.3π 0.1π
(∇× H) · dS = (36 cos θ cos φ)16 sin θ dθ dφ
S 0 0
0.3π 0.1π
576 1 2
= 2 sin θ cos φ dφ
0 0
2
= 288 sin 0.1π sin 0.3π = 22.2A