Page 582 - Engineering Electromagnetics, 8th Edition
P. 582
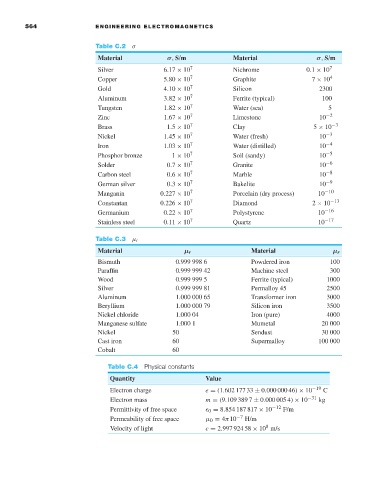
564 ENGINEERING ELECTROMAGNETICS
Table C.2 σ
Material σ, S/m Material σ, S/m
Silver 6.17 × 10 7 Nichrome 0.1 × 10 7
Copper 5.80 × 10 7 Graphite 7 × 10 4
Gold 4.10 × 10 7 Silicon 2300
Aluminum 3.82 × 10 7 Ferrite (typical) 100
Tungsten 1.82 × 10 7 Water (sea) 5
Zinc 1.67 × 10 7 Limestone 10 −2
Brass 1.5 × 10 7 Clay 5 × 10 −3
Nickel 1.45 × 10 7 Water (fresh) 10 −3
Iron 1.03 × 10 7 Water (distilled) 10 −4
Phosphor bronze 1 × 10 7 Soil (sandy) 10 −5
Solder 0.7 × 10 7 Granite 10 −6
Carbon steel 0.6 × 10 7 Marble 10 −8
German silver 0.3 × 10 7 Bakelite 10 −9
Manganin 0.227 × 10 7 Porcelain (dry process) 10 −10
Constantan 0.226 × 10 7 Diamond 2 × 10 −13
Germanium 0.22 × 10 7 Polystyrene 10 −16
Stainless steel 0.11 × 10 7 Quartz 10 −17
Table C.3 µ r
Material µ r Material µ r
Bismuth 0.999 998 6 Powdered iron 100
Paraffin 0.999 999 42 Machine steel 300
Wood 0.999 999 5 Ferrite (typical) 1000
Silver 0.999 999 81 Permalloy 45 2500
Aluminum 1.000 000 65 Transformer iron 3000
Beryllium 1.000 000 79 Silicon iron 3500
Nickel chloride 1.000 04 Iron (pure) 4000
Manganese sulfate 1.000 1 Mumetal 20 000
Nickel 50 Sendust 30 000
Cast iron 60 Supermalloy 100 000
Cobalt 60
Table C.4 Physical constants
Quantity Value
Electron charge e = (1.602 177 33 ± 0.000 000 46) × 10 −19 C
Electron mass m = (9.109 389 7 ± 0.000 005 4) × 10 −31 kg
Permittivity of free space 0 = 8.854 187 817 × 10 −12 F/m
Permeability of free space µ 0 = 4π10 −7 H/m
8
Velocity of light c = 2.997 924 58 × 10 m/s