Page 320 - Engineering Plastics Handbook
P. 320
278 Engineering Plastics
Thermal stability
Polyamide-imides enjoy exceptional thermal stability with a decompo-
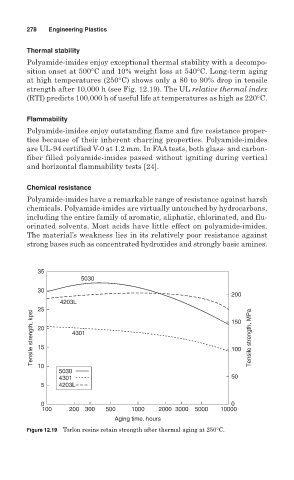
sition onset at 500°C and 10% weight loss at 540°C. Long-term aging
at high temperatures (250°C) shows only a 80 to 90% drop in tensile
strength after 10,000 h (see Fig. 12.19). The UL relative thermal index
(RTI) predicts 100,000 h of useful life at temperatures as high as 220°C.
Flammability
Polyamide-imides enjoy outstanding flame and fire resistance proper-
ties because of their inherent charring properties. Polyamide-imides
are UL-94 certified V-0 at 1.2 mm. In FAA tests, both glass- and carbon-
fiber filled polyamide-imides passed without igniting during vertical
and horizontal flammability tests [24].
Chemical resistance
Polyamide-imides have a remarkable range of resistance against harsh
chemicals. Polyamide-imides are virtually untouched by hydrocarbons,
including the entire family of aromatic, aliphatic, chlorinated, and flu-
orinated solvents. Most acids have little effect on polyamide-imides.
The material’s weakness lies in its relatively poor resistance against
strong bases such as concentrated hydroxides and strongly basic amines.
35
5030
30
200
4203L
25 150
Tensile strength, kpsi 20 4301 100 Tensile strength, MPa
15
10
5030
4301 50
5 4203L
0 0
100 200 300 500 1000 2000 3000 5000 10000
Aging time, hours
Figure 12.19 Torlon resins retain strength after thermal aging at 250°C.