Page 145 -
P. 145
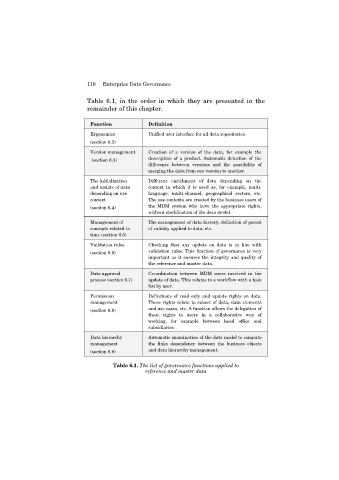
110 Enterprise Data Governance
Table 6.1, in the order in which they are presented in the
remainder of this chapter.
Function Definition
Ergonomics Unified user interface for all data repositories.
(section 6.2)
Version management Creation of a version of the data, for example the
(section 6.3) description of a product. Automatic detection of the
difference between versions and the possibility of
merging the data from one version to another.
The initialization Different enrichment of data depending on the
and update of data context in which it is used as, for example, multi-
depending on use language, multi-channel, geographical sectors, etc.
context The use contexts are created by the business users of
(section 6.4) the MDM system who have the appropriate rights,
without modification of the data model.
Management of The management of data history, definition of period
concepts related to of validity applied to data, etc.
time (section 6.5)
Validation rules Checking that any update on data is in line with
(section 6.6) validation rules. This function of governance is very
important as it ensures the integrity and quality of
the reference and master data.
Data approval Co-ordination between MDM users involved in the
process (section 6.7) update of data. This relates to a workflow with a task
list by user.
Permission Definitions of read only and update rights on data.
management These rights relate to subset of data, data elements
(section 6.8) and use cases, etc. A function allows the delegation of
these rights to users in a collaborative way of
working, for example between head office and
subsidiaries.
Data hierarchy Automatic examination of the data model to compute
management the links dependency between the business objects
(section 6.9) and data hierarchy management.
Table 6.1. The list of governance functions applied to
reference and master data