Page 140 -
P. 140
104 Enterprise Data Governance
depends on the context in which the data model is being
4
used .
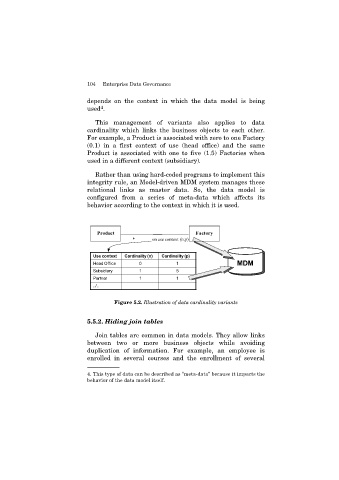
This management of variants also applies to data
cardinality which links the business objects to each other.
For example, a Product is associated with zero to one Factory
(0.1) in a first context of use (head office) and the same
Product is associated with one to five (1.5) Factories when
used in a different context (subsidiary).
Rather than using hard-coded programs to implement this
integrity rule, an Model-driven MDM system manages these
relational links as master data. So, the data model is
configured from a series of meta-data which affects its
behavior according to the context in which it is used.
Usine
Produit
Product Factory
* on use context (n,p)
Use context Cardinality (n) Cardinality (p)
Head Office 0 1 MDM
Subsidiary 1 5
Partner 1 1
../..
Figure 5.2. Illustration of data cardinality variants
5.5.2. Hiding join tables
Join tables are common in data models. They allow links
between two or more business objects while avoiding
duplication of information. For example, an employee is
enrolled in several courses and the enrollment of several
4. This type of data can be described as “meta-data” because it impacts the
behavior of the data model itself.