Page 166 -
P. 166
142 Chapter 5 • Implementation Strategies
Business
Sites
Other
Sites
Border Router
Internet
Perimeter DMZ Web Servers
firewall
Network
Attached Print Reporting Interfaces
Storage Servers
Load Balancers
Application Servers
Secure Network Segment
Application
Firewall
Database Servers
Batch
Scheduler Reporting Production
Third Training Development
Party
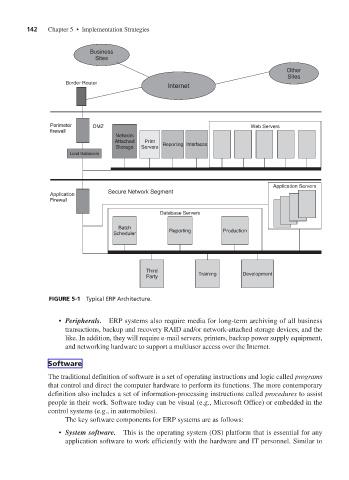
FIGURE 5-1 Typical ERP Architecture.
• Peripherals. ERP systems also require media for long-term archiving of all business
transactions, backup and recovery RAID and/or network-attached storage devices, and the
like. In addition, they will require e-mail servers, printers, backup power supply equipment,
and networking hardware to support a multiuser access over the Internet.
Software
The traditional definition of software is a set of operating instructions and logic called programs
that control and direct the computer hardware to perform its functions. The more contemporary
definition also includes a set of information-processing instructions called procedures to assist
people in their work. Software today can be visual (e.g., Microsoft Office) or embedded in the
control systems (e.g., in automobiles).
The key software components for ERP systems are as follows:
• System software. This is the operating system (OS) platform that is essential for any
application software to work efficiently with the hardware and IT personnel. Similar to